 Atmospheric Environmental Particle Monitoring
Atmospheric Environmental Particle Monitoring
Air pollutants such as desert dust and PM2.5, volcanic ash and forest fire, greatly influence our living environment. These atmospheric fine particles (called "aerosols") cause poor visibility, damage to cars, houses and agricultural products, and health hazard. Using various satellite data over the world, EORC estimates aerosol optical thickness (atmospheric turbidity index) and the Ångström exponent (aerosol particle size index) and provides the data products and images to researchers and general users. We aim to build, in coordination with external organizations, a system that predicts when, from where, to where and what concentration the aerosol comes by air, by building a data assimilation system where satellite data is incorporated into the aerosol transport model.
 Yellow Sand swirls in the wind, floats in the air, and affects global climate.
Yellow Sand swirls in the wind, floats in the air, and affects global climate.

Hiroshi Murakami
Senior Researcher
Associate Fellow
Earth Observation Research Center
Space Technology Directorate 1

Maki Kikuchi
Researcher
Earth Observation Research Center
Space Technology Directorate 1
Aerosol Observation using Satellites

The above images show the eruption of Asosan Mountain observed by TANSO-CAI sensor onboard the Greenhouse Gases Observation Satellite (GOSAT) "IBUKI" on November 17, 2015.
Atmospheric Particle Aerosol affecting natural environment and human lives
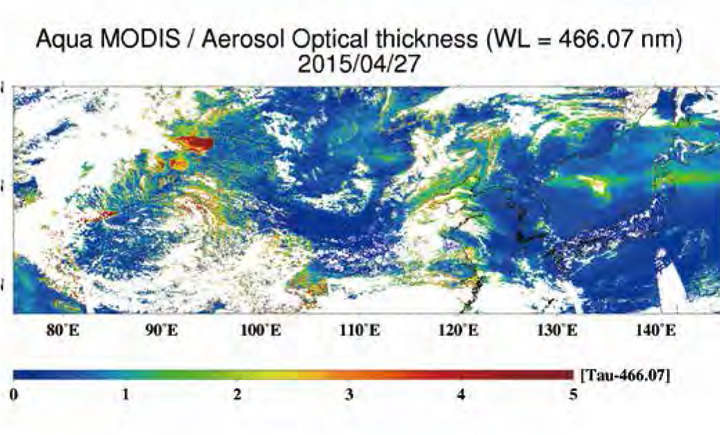
Aerosol optical thickness observed using the MODIS sensor loaded on the Earth Observation Satellite "Aqua" on April 27, 2015 Smoke from forest fires in China passing over the Northeast Japan is clearly seen.
Yellow Sand Example in East Asia Area on April 15, 2015
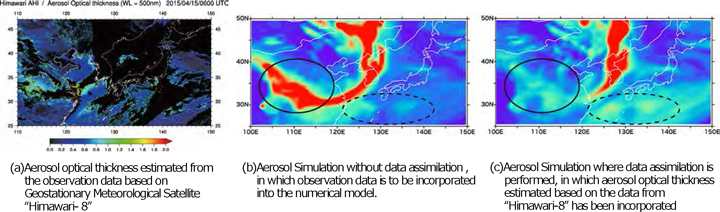
It is clearly understood that overestimation of the inland area in China (inside the solid line) and underestimations of the south of Japan (inside the broken line) have been improved by implementing the observation of Himawari-8 in the simulation.
*The aerosol simulation is achieved as the result of using the aerosol transfer model (MASINGAR) in the meteorological Research Institute of Japan Meteorological Agency.



