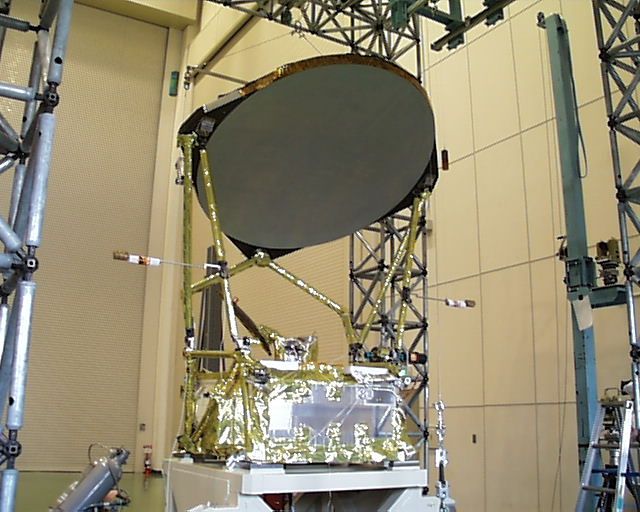
NASA Aqua Satellite (AMSR-E mounted)
Mission
An Earth-observation satellite to contribute to the understanding of the Earth's water cycle
Aqua is a NASA earth observation satellite that, as its name suggests, monitors from space various kinds of physical phenomena related to water and energy circulation. It conducts comprehensive observations of the interactions among the atmosphere, the oceans and the continents, and their effects on changes in the Earth's mechanism. Data gathered by this satellite include profiles of atmospheric temperature and humidity, clouds and precipitation, net radiation, snow and sea ice, sea-surface temperature, oceanic primary production, and soil water. These accumulated data are expected to be used to promote the further development of research on global environmental change, as well as to improve numeric weather forecasts.
International Project
Aqua was developed as a joint project by the United States, Japan and Brazil. It was launched from the Vandenberg Firing Range in California by the DELTA II launch vehicle in May, 2002. NASA was responsible for the spacecraft and its launch, while Japan and Brazil were in charge of various sensors. JAXA developed a radio sensor and the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for EOS (AMSR-E), which is helping obtain data to understand global-scale water and energy cycles.
