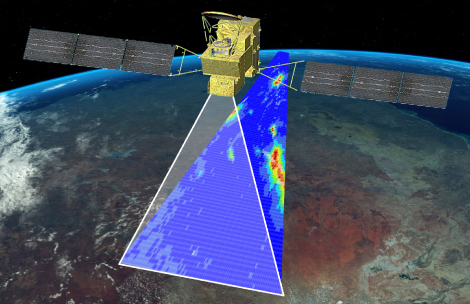
Global Observing Satellite for Greenhouse Gases and Water Cycle
GOSAT-GW (AMSR3 mounted)
Mission
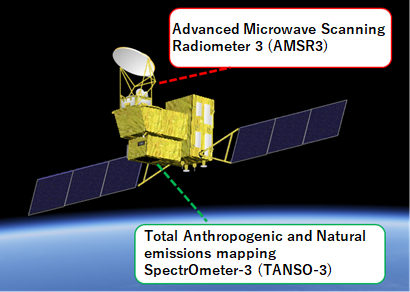
The Global Observing SATellite for Greenhouse gases and Water cycle (GOSAT-GW*1) is an Earth observation satellite that is responsible for the greenhouse gases observation missions (led by the Japanese Ministry of the Environment and the National Institute for Environmental Studies) and the water cycle variation observation missions (led by JAXA). In order to continue and expand missions on the water cycle variation observation by SHIZUKU (GCOM-W*2, launched in 2012) and on the greenhouse gases observation by IBUKI (GOSAT*3, 2009) and IBUKI-2 (GOSAT-2*3, 2018), GOSAT-GW will carry two successor sensors, the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer 3 (AMSR3) developed by JAXA, and the Total Anthropogenic and Natural emissions mapping SpectrOmeter-3 (TANSO-3) developed by JAXA under contract with the Ministry of the Environment. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation is selected as the primary manufacturer of the satellite and its onboard sensors.
- GOSAT-GW: The Global Observing SATellite for Greenhouse gases and Water cycle
- GCOM-W: The Global Change Observation Mission – Water
- GOSAT: The Greenhouse gases Observing SATellites
Mission Instrument
Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer 3 (AMSR3)
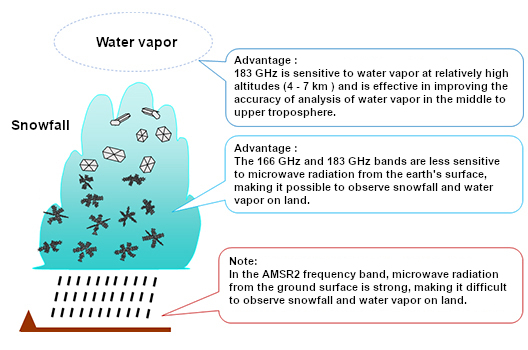
AMSR3 is a sensor that observes microwaves naturally emitted from the earth's surface, ocean surface, and atmosphere. AMSR3 enhances the observable wavelength band from AMSR2 on GCOM-W to enable observations of snowfall and water vapor on land.
AMSR3 Technology
AMSR3 Technology
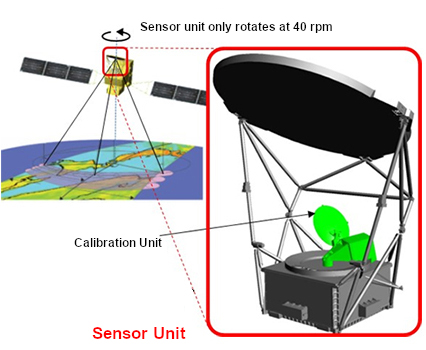
The Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer 3 (AMSR3) to be mounted on GOSAT-GW is the successor to the AMSR2 sensor mounted on GCOM-W, and aims to achieve the world's top performance and functionality as a microwave radiometer. Microwave radiometers can observe physical quantities related to water on the ground surface, sea surface, and in clouds through the clouds. AMSR3 is also capable of nighttime observations, making it possible to perform observations at any time of the day or night, regardless of weather conditions. AMSR3 is equipped with the new 166 GHz and 183 GHz bands, which will improve the accuracy of analysis and enable observations of snowfall and water vapor on land.
Total Anthropogenic and Natural emissions mapping SpectrOmeter-3 (TANSO-3)
TANSO-3, which is being developed by the Ministry of the Environment, is the successor sensor to TANSO-FTS-2 *4 installed on "IBUKI-2". By replacing the Fourier interferometric spectrometer used in TANSO-FTS-2 with a new diffraction grating spectrometer, TANSO-3 will be able to observe more spatially detailed greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). TANSO-3 will also newly observe nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
- TANSO-FTS-2: Thermal And Near infrared Sensor for carbon Observation - Fourier Transform Spectrometer-2
TANSO-3 Technology
TANSO-3 Technology
TANSO-3, which will be mounted on GOSAT-GW, is the successor to TANSO-FTS-2, which was mounted on IBUKI-2, and will contribute to improving the accuracy of estimating greenhouse gas emissions by observing a wide range of greenhouse gases on the earth with high accuracy. The main feature of TANSO-3 is that it adopts a new diffraction grating spectroscopy method instead of the Fourier interferometric spectroscopy method used in TANSO-FTS and TANSO-FTS-2. This new grating type spectroscopy method enables observation over an area, whereas the previous method was based on a grating of points, and thus enables more observation data to be acquired. TANSO-3 is equipped with two observation modes: wide-area observation mode and precise observation mode. The wide-area mode enables areal observations with a resolution of 10 km over a swath of more than 911 km, while the precise mode enables detailed observations with a resolution of 3 km over a swath of more than 90 km.