Seen from Space 2008
Blossoming Renaissance in Florence
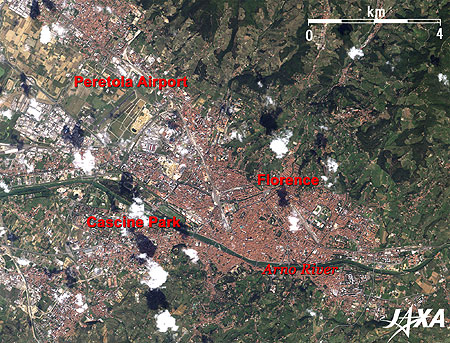
The Arno River flows through from right (East) to left (West) in the figure. The river flows into the Tyrrhenian Sea, part of the Mediterranean Sea, and western Italy, from Mount Falterona in the middle of Italy. At the mouth of the river is Pisa, which is famous for the Leaning Tower (77km west of Florence and not included in this figure). Central Florence is distinguished by numerous red-bricked roofs. Yellow and light green areas represent wheat and grape fields. The grape-growing district for famous Chianti wine in Tuscany extends across the bottom (South) of the full image. The deep-green area is a vast forest. Florence thus gives the impression of an old red city surrounded by nature. You can see the largest park in Florence, Cascine Park (named cow house), in the lower left side of the figure. A small international airport, Amerigo Vespucci or Peretola Airport, is visible on the left side.
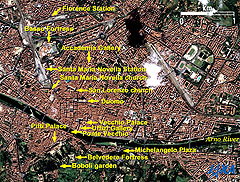
Some remarkable buildings are visible in the center of the figure. They are the Santa Maria del Fiore Cathedral has Duomo as a symbol of Florence. The Cathedral is composed of the Cathedral itself, a bell tower, and a chapel just like the cathedrals in Pisa and Siena that competed in the 13th to 14th century. The leaning tower in Pisa is known, but the Duomo with Cupola (it means dome in Italian, is 43m in internal diameter, and stands 108 meters tall) in Florence is also very popular. The Cathedral is called the Florence Cathedral, the Santa Maria del Fiore Cathedral and simply Duomo. The cupola of the Duomo was the largest dome built at that time. Filippo Brunelleschi, designer of the cupola, was applauded as a symbol of the Renaissance. The attractive beautiful façade of the Duomo is covered in white, green and red marble in a geometric pattern. The 82-meter-tall bell tower is called Giotto's Bell Tower. It was named after a designer, Giotto. The chapel named San Giovanni is octagonal, is older than the Duomo, and was used as a cathedral before the Duomo was built. The whitish round building on the right is the Cupola of the Duomo, and the slender building on the left is a part of the Duomo. The Cupola seems whitish due to strong sunlight from the southeast, but it is actually made of red bricks. The round (actually octagonal) building on the left of Duomo is a chapel, and the small building visible in the left bottom of the Duomo is Giotto's Bell Tower. Just above of Duomo is San Lorenzo church, which was updated by Brunelleschi. Vecchio Palace below Duomo was a government office of the Firenze Republic. It was an old palace of the Medici family (1360-1737) and is even now a city office of Florence. Vecchio means old in Italian. Uffizi Gallery is below the palace. Uffizi means office in Italian. Cosimo I de' Medici (1519-1574), a member the of Medici family, annexed Siena, was Grand Duke of Tuscany in 1569, and commuted there every day. As the Medici extinguished, Anna Maria Lodovica, the last Medici heiress, presented several thousands of Medici's art treasures under the condition that they remain in Florence and open to the public. A collection of the works of great Italian Renaissance painters such as Sandro Botticelli, Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo and Raphael can be found in the gallery. The Birth of Venus by Botticelli is displayed in the Botticelli room, the largest room in Uffizi. The whole building forms a huge U. Signoria Plaza is visible between Vecchio Palace and Uffizi Gallery. Pitti Palace, formerly the residence of the Medici family, is located on the south bank across the Arno River. It is simple but big, has a large Boboli garden, and is now the home of art galleries and museums. It was ordered by Luca Pitti, a Florentine banker; designed by Brunelleschi; and then bought by the Medici family in the 16th century. The Ponte Vecchio (Italian for Old Bridge) is a bridge over the Arno River between Pitti Palace and Uffizi. It was built in 1345 and is the oldest bridge in Florence. A private corridor, Vasari Corridor, was built for Cosimo I de' Medic on second floor to enable him to move freely from his residence to his office out of sight of his many political rivals, and is now a gallery. Michelangelo plaza is located on a small hill to the right of Boboli garden and overlooks Florence city. Firenze Station and Santa Maria Novella Station (Central Station) are visible in the upper left of Fig. 2. Santa Maria Novella Church is just below the Santa Maria Novella Station. It is a church but also the world's oldest pharmacy. It started in 1221 with the cultivation of herbs in Dominican monasteries. It continues to produce eau de Cologne, soap and body care goods, after licensed pharmacy in 1612 and purveyor to the Medici family. It is also known that Leonardo da Vinci lived here for three years while painting the Mona Lisa. Accademia Gallery is on the right of Santa Maria Novella Station. Here stands the well known 4m tall statue of David by Michelangelo. The statue was originally in the Signoria Plaza but was transferred here in 1873. Florence is surrounded by a castle wall and has many towers and fortresses. Basso Fortress and Belvedere Fortress are visible in the figure. Basso Fortress used to be the venue of exhibitions and meetings. Belvedere Fortress sits on a low hill and is a good place for viewing Florence. A large sports complex for football and baseball is also visible on the right of the figure. Central Florence was added to the list of World Cultural Heritage sites of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 1982 as the Historic Centre of Florence.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||