| |
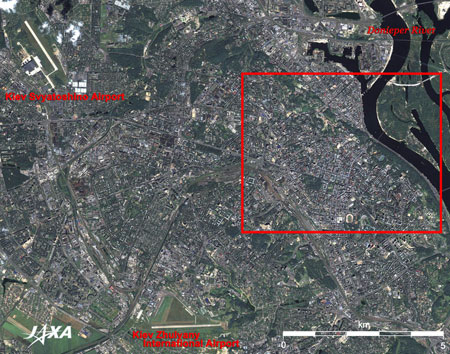
Figure 1 depicts the vicinity of Kiev, the capital of Ukraine. The figure was produced by combining two images acquired simultaneously by the Advanced Visible and Near Infrared Radiometer-2 (AVNIR-2) and the Panchromatic Remote-sensing Instrument for Stereo Mapping (PRISM) on board the Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) "Daichi" in August 2006. The black Dnieper River flows from north to south in the upper right of the figure. The bridges spanning the Dnieper River are, from north to south, a road bridge, a railway bridge, and two pedestrian bridges. A plinth of a bridge under construction is visible to the east of the port in a canal. Two airports are visible in the figure. Kiev Svyatoshino Airport is in the upper left, and Kiev Zhulyany International Airport, former gateway to Kiev, is in the bottom. Zhulyany's gateway function, however, was transferred to the larger Kiev International Airport (Boryspil Airport; visible in the right of the full image), which was constructed in the 1960s on the east side of the Dnieper River. Flights to Kiev from Japan are only available via main airports in Europe. The brownish-grey curved line, running from the lower left to the center of the figure and going down to the lower right, is a railway. Kiev station is located where the railway turns toward the lower right.
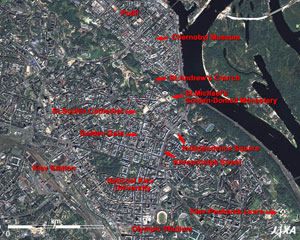 |
Fig. 2 Close up of Central Kiev
Kiev,Ukraine (kmz, 1.42MB, Low Resolution) as seen on Google Earth. |
 |
 |
| Fig. 3 Independence Square |
Fig. 4 St. Sophia Cathedral |
Kiev is the oldest city in the East Slavic, with a history of more than 1500 years. The area in the west coast of the Dnieper River is the downtown area of Kiev, whose center is the Independence Square (Fig. 3). This square extends over Khreschatyk Street. The north side is the old square, and the south side, with an underground shopping mall, was constructed in 2001, ten years after the national foundation. The 52m-high Ukraine Independence Monument and its shadow are visible in the center of the south square. St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery, commonly called the "Blue Church," is located to the north of Independence Square, and its seven dotted gold domes towering from the monastery roof of the Cathedral, are visible. Located at the end of the street running west from the Monastery is St. Sophia Cathedral (Fig. 4), the oldest church now existing in Kiev, having been built in 1037.
Located to the north of St. Sophia Cathedral is St. Andrew's Church, which was designed and built in the mid 18th century by the architect Bartolomeo Rastrelli from Italy whose major works are the Winter Palace and the Summer Palace in St Petersburg. Andrew's Slope, which goes down to the northwest from this church, is crowded with tourists and street stalls selling souvenirs. The area at the foot of the slope is the Podil, the former business district, where rows of low houses and old buildings reflect a vestige of the historic city. The Chernobyl Museum is in this district. An explosion occurred at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant 20 years ago (in 1986), 100km north of Kiev.
The 5km long hilly area along the Dnieper River on the east of Independence Square is the green Wladimir Park. The hills in the downstream area are the "forest of monasteries" where golden domes including Kievo-Pecherskaya Lavra (Kiev Monastery on the Caves) stand close together. Kiev: Saint-Sophia Cathedral and Related Monastic Buildings, Kiev-Pechersk Lavra was added to the World Heritage list of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 1990.
 |
| Fig. 5 National Kiev University |
National Kiev University (Fig. 5) is located east of the pentagonal green park and Kiev Station at the lower left of the figure. The facades of the buildings are painted crimson, the color of blood, and are relics of the order from Nicholas I of Russia as a punishment to the students who fomented a military draft refusal movement.
The Golden Gate is located two blocks from the National Kiev University toward St. Sophia Cathedral. This is where the formal entrance of the castellated wall surrounding Kiev was located in the early 11th century. A Mongolian army destroyed it in 1240, and a new gate was rebuilt in 1982 to preserve the ruins of the gate enclosed inside.
The Olympic Stadium built for the Moscow Olympics held in 1980 is visible at the bottom of the figure. Fifty countries, including the United States, China, and Japan, boycotted the Moscow Olympics in protest against the invasion of Afghanistan by the Soviet Union. The first-round matches and quarterfinal match of the football games were held here. This stadium is the biggest stadium in Ukraine, and has accommodated up to 100,000 attendants (83,000 now) at the beginning.
Kiev was always historically torn between Russia and Europe, divided into six major periods. These periods are, from the ancient time to the present, the period of Scythia and Sarmatia from the 6th century B.C. to 4th century A.D., Kievan Rus' period from the 4th - 6th century to the Mongolian army destruction in 1240, the Ukraine Cossack period in the 14-16th century, the period of the Russian Empire in the 16-19th century, the subsequent Soviet Union period, and the period up to independence in December 1991. The division-of-work policy of the Soviet Union era called for Ukraine to support war industries, such as steel, shipbuilding, and aerospace industries, so the level of science and technology there seems to be extremely high. Moreover, Ukraine also produced grain for the Soviet Union. Ukraine is expected to be one of the countries that saves the world from a food crisis in the 21st century (*).
| (*) Historic Story of the Ukraine, Chuko-Shinsho 1655, by Yuji Kurokawa |
Explanation of the Image:
(Figs. 1 and 2)
PRISM is an optical sensor for observing ground surfaces with visible and near-infrared signals in the 520 to 770 nano-meter (one-billionth of a meter) band. The acquired image is monochrome. PRISM has three independent optical systems (telescopes) to acquire images for nadir, forward, and backward views at the same time. Only the nadir image was used in this article.
AVNIR-2 is equipped with a pointing function by which it can shift its observation area perpendicular to the ALOS's moving direction, and it can observe ground surfaces with four spectral bands.
First, the color image was produced by assigning red to Band 3(610 to 690 nm), green to Band 2 (520 to 600 nm), and blue for Band 1 (420 to 500 nm). Then, the image was transformed into Hue, Saturation and Intensity, and the Intensity was replaced by the PRISM image. The Hue, Saturation and Intensity data were then reversed into a color image. As a result, a virtual 2.5 m ground-resolution color image was obtained. This kind of high-resolution color image, composed by combining the higher resolution monochrome image and the lower resolution color image, is called a pan-sharpened image. The resulting image has natural coloring as if seen by the naked eye. In this image, forests are deep green, grass fields or farms are light green, bare grounds are ocher, roads are grey, and roofs are colors as they are.
The full image is the original AVNIR-2 scene used for producing pan-sharpened images. The coloring is white for clouds, blue for rivers or lakes, khaki or brown for farms, grey for urban area, and black for areas with no data.
|
 |
|