- Top
- Technical development
- Satellite platform and instruments
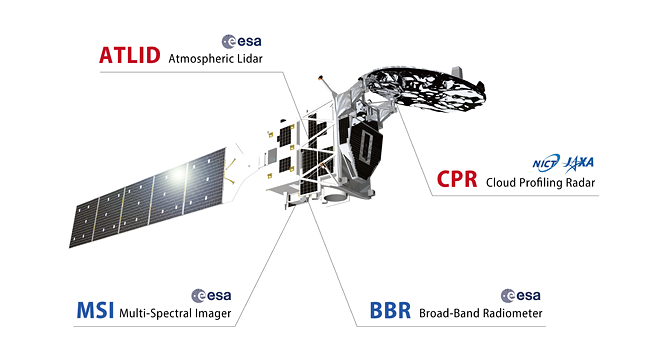
EarthCARE is a joint mission between Japan and Europe. The European Space Agency (ESA) is responsible for the development, launch, and operation of the satellite itself. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) developed the Cloud Profiling Radar (CPR), the world's first spaceborne Doppler radar for cloud observation. ESA developed the Atmospheric Lidar (ATLID), the Multi-spectral Imager (MSI), and the Broadband Radiometer (BBR).
| Development agency | European Space Agency (ESA) / National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) / Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) | |
| Launch | 28 May 2024 (UTC) | |
| Design lifetime | 3 years | |
| Mass | Satellite Approx. 1960 kg, Propellant approx. 310 kg | |
| Average power consumption | Approx. 1645 W | |
| Data rate | ~2.5 Mbps | |
| Attitude control | Three-axis stabilised, yaw-steering control | |
| Satellite orbit | Orbit | Sun-synchronous sub-recurrent orbit |
| Local crossing time (descending) | 14:00 | |
| Altitude | Approx. 393 km (at the equator) | |
| Inclination | 97.05 degrees | |
| Cycle | Approx. 92.5 min. | |
| Revisit time | 25 days | |
Instruments onboard EarthCARE
| Name of equipment | Equipment Overview | Sensing method |
|---|---|---|
|
CPR
Cloud Profiling Radar
|
CPR is the world's first spaceborne Doppler radar jointly developed by JAXA/NICT which observes the vertical distribution of clouds and weak rainfall, as well as their upward and downward motions. |
Active sensor
Transmits millimeter-wavelength radio pulses (94 GHz, W-band) in and receives scattered signals from particles.
|
|
ATLID
Atmospheric Lidar
|
ATLID is a High Spectral Resolution Lidar (HSRL) observes vertical distribution and shape information of clouds and aerosols. |
Active sensor
Transmit laser pulses in the ultraviolet wavelength (355 nm) and receives scattered signals from particles.
|
|
MSI
Multi-Spectral Imager
|
MSI is an imager (pushbroom optical scanner) which has sensitivity in the visible to thermal infrared region and observes the horizontal distribution of clouds and aerosols with a scanning range of 150 km. |
Passive sensor
Receives reflections and emissions from the earth's surface in 7 channels in the visible to thermal infrared range.
|
|
BBR
Broad-Band Radiometer
|
BBR is a radiometer sensitive in broad range of wavelength which observes radiation balance in the two separated bands (long and short wave bands). |
Passive sensor
Receives reflections and emissions from the earth's surface in both shortwave and longwave broadband bands.
|
The EarthCARE satellite will be equipped with four different types of instruments (radar, lidar, imager, and radiometer) to study the three-dimensional structure of clouds and aerosols in the Earth's atmosphere and their interactions. Synergistic (synchronized) observations by the four instruments will enable us to obtain observation data from each sensor at almost the same location and time.
The observation data obtained from each sensor is processed by higher-order processing algorithms into not only a single sensor product, but also a two-sensor composite product, a three-sensor composite product, a four-sensor composite product, and so on, and provided to the user.