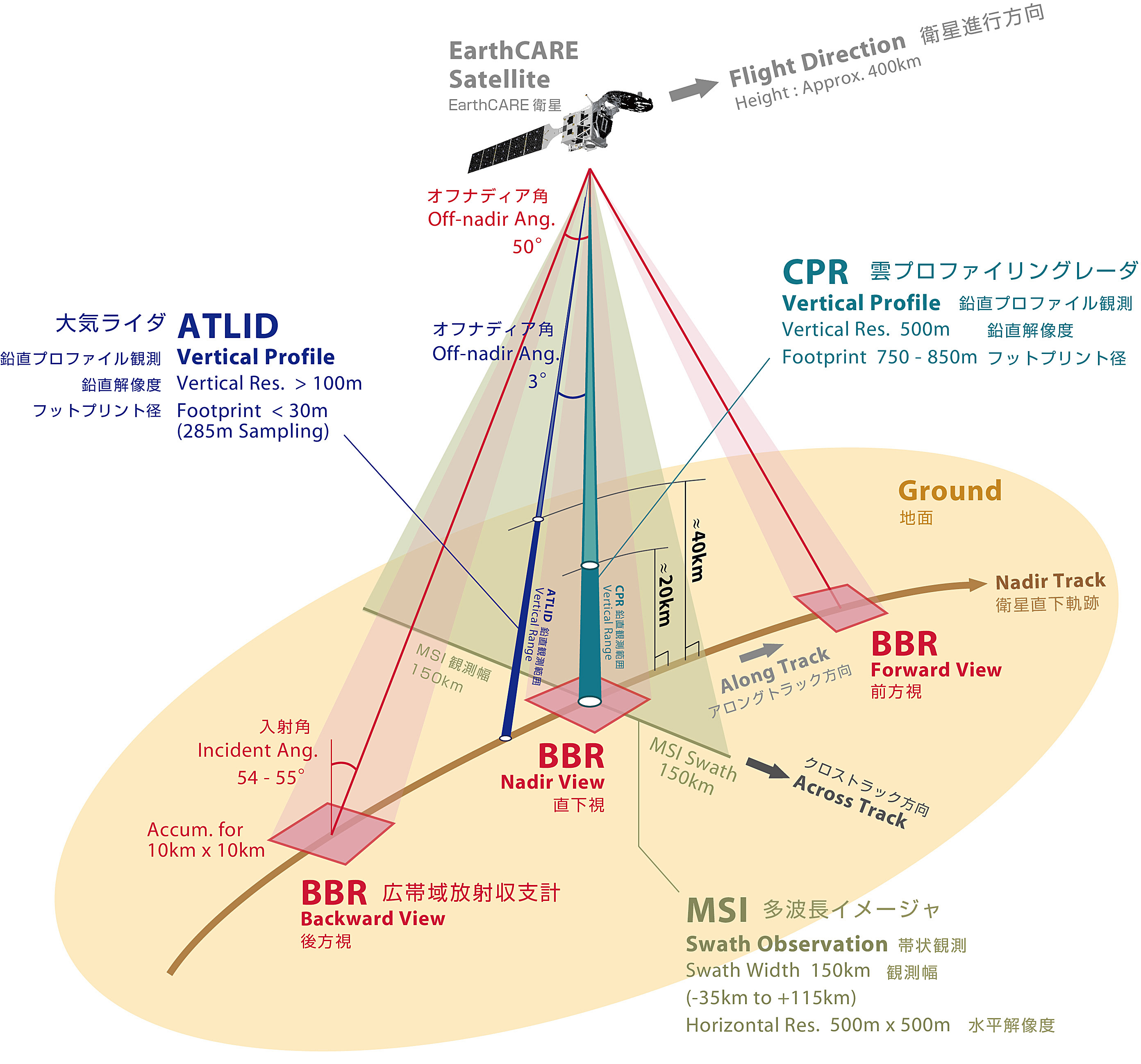
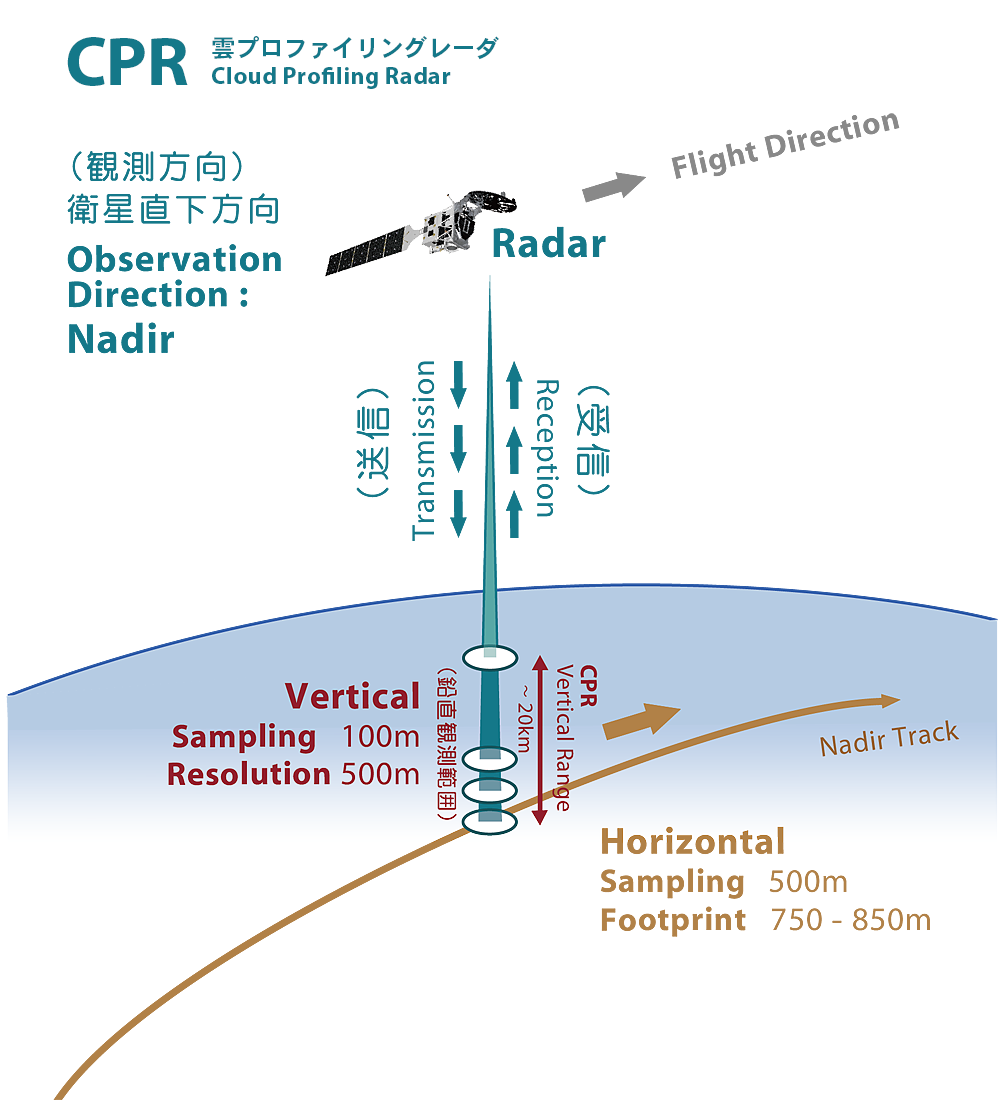
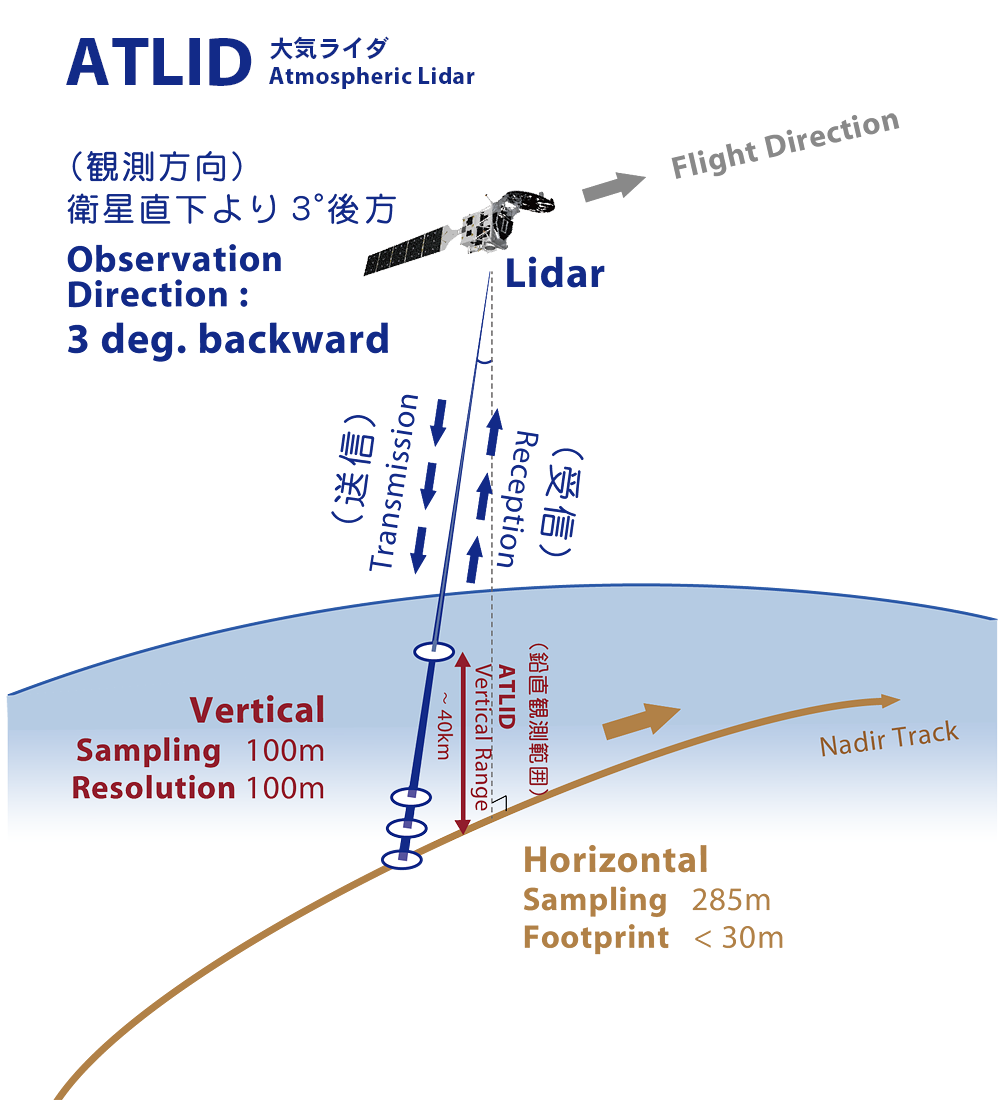
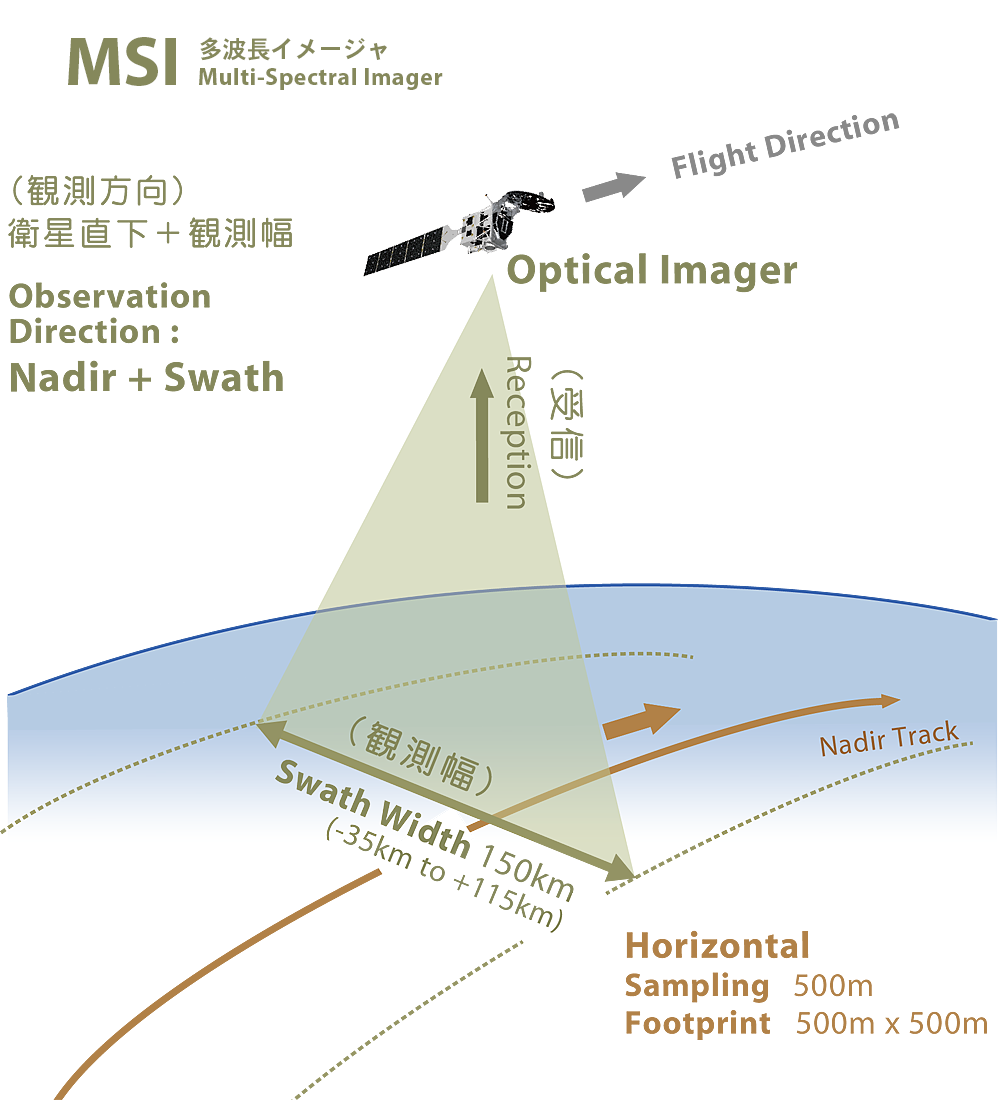
CPR and ATLID are active sensors that detect targets by transmitting signals toward the Earth's surface (including clouds and aerosols), and detect information according to the distance in the line-of-sight direction (direction of signal transmission: generally vertical). CPR acquires vertical distribution data from the ground to an altitude of up to 20 km, while ATLID acquires vertical distribution data from the ground to up to 40 km.
The CPR's line of sight is directly below the satellite, while the line of sight of ATLID is 3 degrees behind the satellite, the corresponding difference of distance is about 20 km near the surface, or about 3 seconds in time. This difference is almost negligible from the perspective of understanding cloud and aerosol dynamics by satellite.