| |
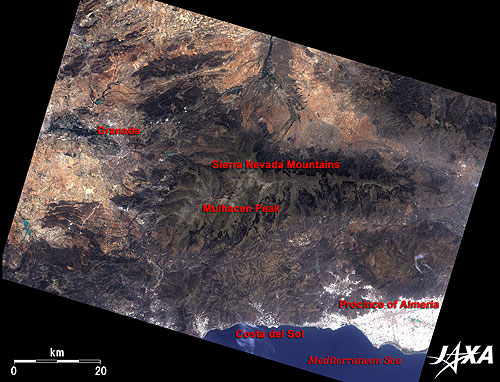 |
| Fig. 1 Vicinity of Granada in Andulsia |
Figure 1 depicts the vicinity of Granada in southern Spain as observed in July 2006. Nestled between the mountains at the central left of the figure, Granada is the capital of the province of Granada, which faces the Mediterranean Sea, in the autonomous region of Andalusia in the Iberian Peninsula. It is renowned as an old city with a rich historical heritage such as Alhambra. The mountain range in the center of the figure is the Sierra Nevada Mountains. The beautiful scene of the old cityscape against the snowcapped mountains is breathtaking. As seen from the figure, snow almost disappears in summer except in little snowy gorges near Mulhacen Peak (3,482m), the highest peak on the Iberian Peninsula. The deep-blue ocean in the lower right of the figure is the Mediterranean Sea. Costa del Sol (Sunny Coast), more than 300km long, is famous for exclusive resorts along the beautiful coastline of the Mediterranean. The glaring white area on the coast is a cluster of roofs of plastic greenhouses that reflect sun light quite strongly (*1). The Province of Almeria has a flourishing agricultural industry of cultivating tomatoes and green peppers in such a huge number of greenhouses that the entire Peninsula of Almeria looks pure white. The huge scale of the greenhouse cultivation can be recognized from the image.
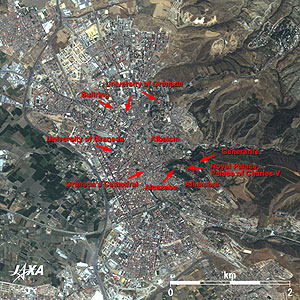 |
Fig. 2 Close-up of Granada City Area
Granada (kmz,2.03MB,Low Resolution) is seen from Google Earth. |
Figure 2 is a close-up image of central Granada. The superb Alhambra is visible on a green hilly terrace at the center of the figure. This Moorish citadel and its palaces were built during the 12th to 14th centuries of the Nasrid Dynasty in the period of Islamic dynasties and is described as a masterpiece of Islamic architecture. The name Alhambra, signifying in Arabic the red (Al Hamra الحمراء), derives from the color of the stones containing a lot of sinopite of which the wall is made. The buildings of the Alhambra were originally whitewashed, but the buildings seen today are reddish. Its afterglow of the oldest citadel is seen at Alcazaba, on the west side of the palaces. The royal palace (Palacios Nazaries) is located in the center of Alhambra, and a square building with a round inner courtyard beside it is the Renaissance style Palace of Charles V (Carlos V). It was constructed by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, after the fall of the Islamic dynasties. The detached palace on a hill in the east of Alhambra is Generarife (Palacio de Generalife), the most beautiful Islamic garden composed of acequias and fountains.
The guitar classic "Alhambra Remembrances (Recuerdos de la Alhambra)" was composed by Francisco Tárrega. He wrote this in the motif of the fountain in the courtyard and arabesque on the walls by which he was inspired when he visited these palaces. This piece of music is known worldwide as one of the most beautiful in the tremolo rendition that reminds us of the cool sound of restless water.
The street of Albaicin (or Albayzín) extends to the north side of the palaces. This area is the oldest town in Granada. White-walled houses, that recall the Islamic age, stand side-by-side along the narrow slope. The maze-like complex townscape can be seen from the satellite image.
Summer heat in southern Spain is severe, but Granada's climate is rather mild as it is located at the center of fertile highland plain called "vega" about 700m above the sea.
Back in the city, Granada's Cathedral (a mixture of Gothic and Renaissance styles), a bullring and the University of Granada (established in 1531) are visible. Granada is famous today as an academic city where 60 thousand of a total population of 250 thousand are students.
Alhambra and Generarife were added to the World Heritage List of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) for their universal architectural value in 1984, and the Albaicin district was added to the list in 1994 (Alhambra, Generalife and Albayzín, Granada (1984, 1994)). Granada is a most typical Spanish city with stratified cultural heritages of Islamic and the Christian cultures.
|
(*1) Sensor detectors are saturated by the strong light from high-illuminance bodies, and images become white. |
Explanation of the Images:
Figs. 1 and 2
AVNIR-2 has four observation bands. The composite images are produced by assigning red to Band 3 (610 to 690nm), green to Band 2 (520 to 600nm), and blue to Band 1 (420 to 500nm). The resulting image has natural coloring as if seen by the naked eye. Thus, the following colors designate ground objects.
| Dark brown: |
Forests |
| Light brown or dark green: |
Grass fields, farmlands |
| Bluish grey: |
City area, roads |
| White: |
Plastic greenhouses, clouds |
| Blue: |
Sea |
| Green: |
Lakes |
| Red: |
Roofs |
|
 |
|






