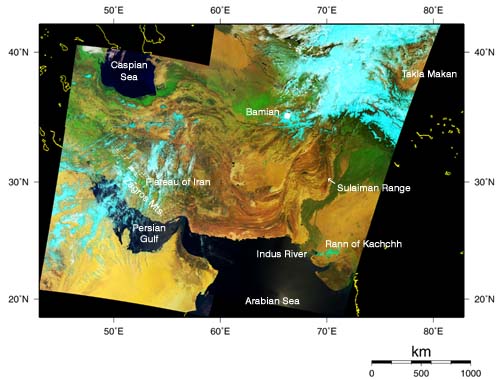
 |
The reddish brown landform is clearly visible in the middle of this image. This is a great fold structure extending to the arid highlands in Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Iran. The western part of this fold is composed of the Zagros Mountains and Iran Plateau, and the eastern part, the Sulaiman Range. East of this, the vegetation-rich area along the Indus River appears vivid green. The south coast of the Caspian Sea (upper left), the western side of Taklimakan (upper right), the eastern side of Saudi Arabia (lower left), and the westrn part of India (lower right) can be seen. The Persian Gulf and the Arabian Sea appears in black from the lower left to the lower center of this image. Yellow areas in the image correspond to desert, and white areas, to clouds. Light blue area primarily represent clouds or snowcover, but the arid salt lake called Rann of Kachchh also appears in light blue on the eastern side of the Indus estuary.
The regions from South Europe to this area, and from north of the Himalayan Range to the Maley Peninsula composed the sea called the Tethys Sea or Paleo-mediterranean Sea from the Jurassic Period to the Cretaceous Period (from 210 million to 65 million years ago), when dinosaurs were still alive. Oil and natural gas are formed from animals, plants, and microbes deposited on the seabed during this age. Later, as part of the Alps mountain range formation, 40million to 50 million years ago, the Indian plate carrying the Indian subcontinent crushed against the Eurasian plate(*). The sea bottom was lifted, and the Tethys Sea gradually dried up; the mighty folded mountain range through the Himalayan Mountains and Pakistan to Iran was thus formed. Thanks to this mountain formation, oil and natural gas were trapped inside, and oil fields were produced on the Gulf coast of Persia and around the Caspian Sea.
In addition, Bamiyan Valley with its Buddhist temple ruins, which was officially designated as a world heritage site on July 2, is located a little to the right of center in the image.
We combined the data acquired by GLI on April 6, 12, and May 2, 2003, and made this false-color image. The picture was generated from GLI spectral channel 29 (2210nm) in red, channel 23 (825nm) in green, and channel 20 (460nm) in blue.
* Plate tectonics is a field of study that explains various changes of the Earth's structure like earthquakes and mountain building, by the relative movement of plates that cover the Earth's surface. |