Image Library
Observation Results of ALOS/PALSAR Relating to the Magnitude 7.6 Earthquake in the South Island, New Zealand (2)
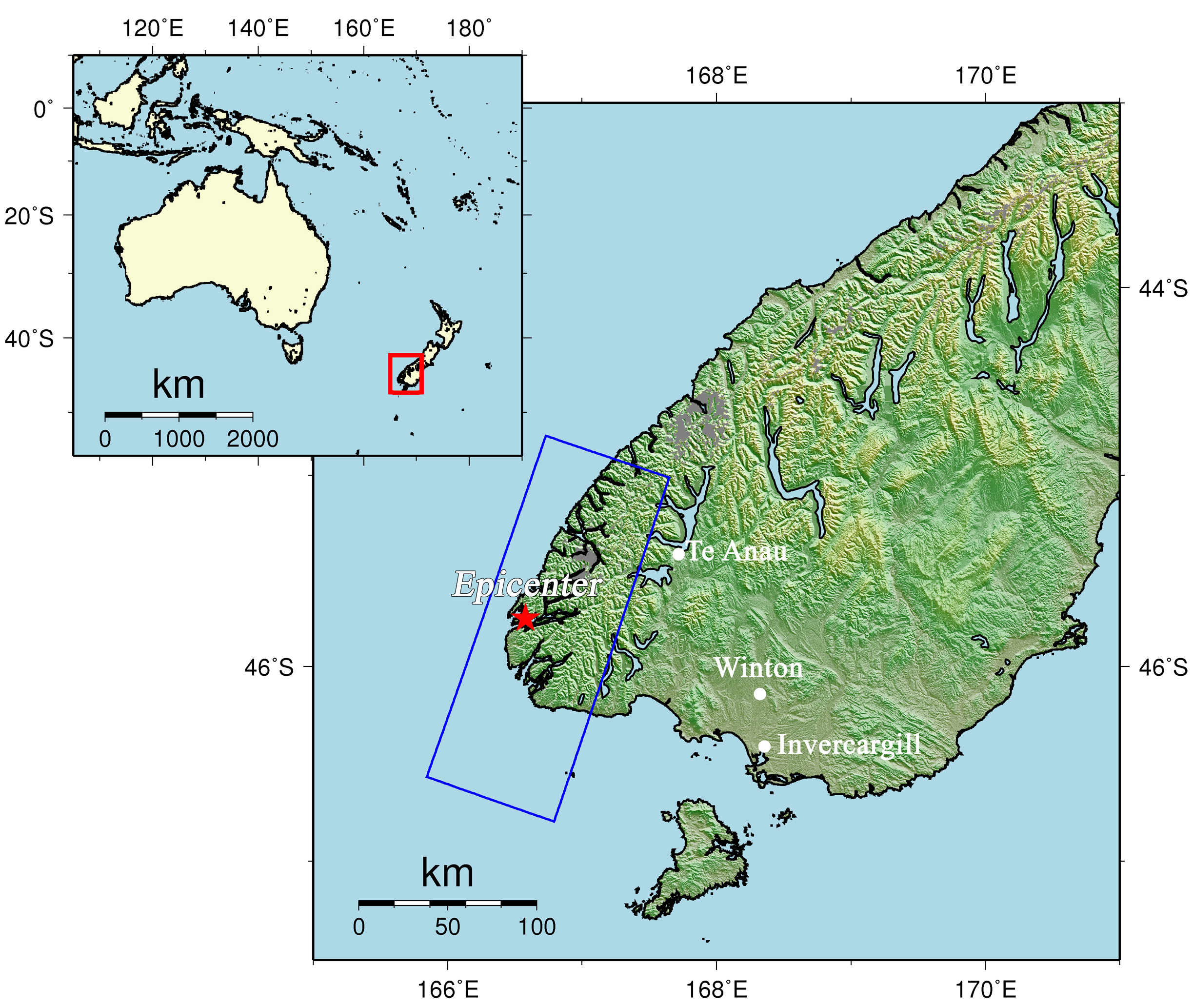
On July 15, 2009 (UTC), a magnitude 7.6 earthquake occurred off the southwest coast of the south island, New Zealand. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) performed an observation on July 23, 2009, using the Phased Array Type L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) installed on the Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) to observe the damage caused by the earthquake. In this report, we conducted differential interferometric SAR (DInSAR) analysis to detect crustal deformation using the data acquired on July 23, 2009 and July 20, 2008.
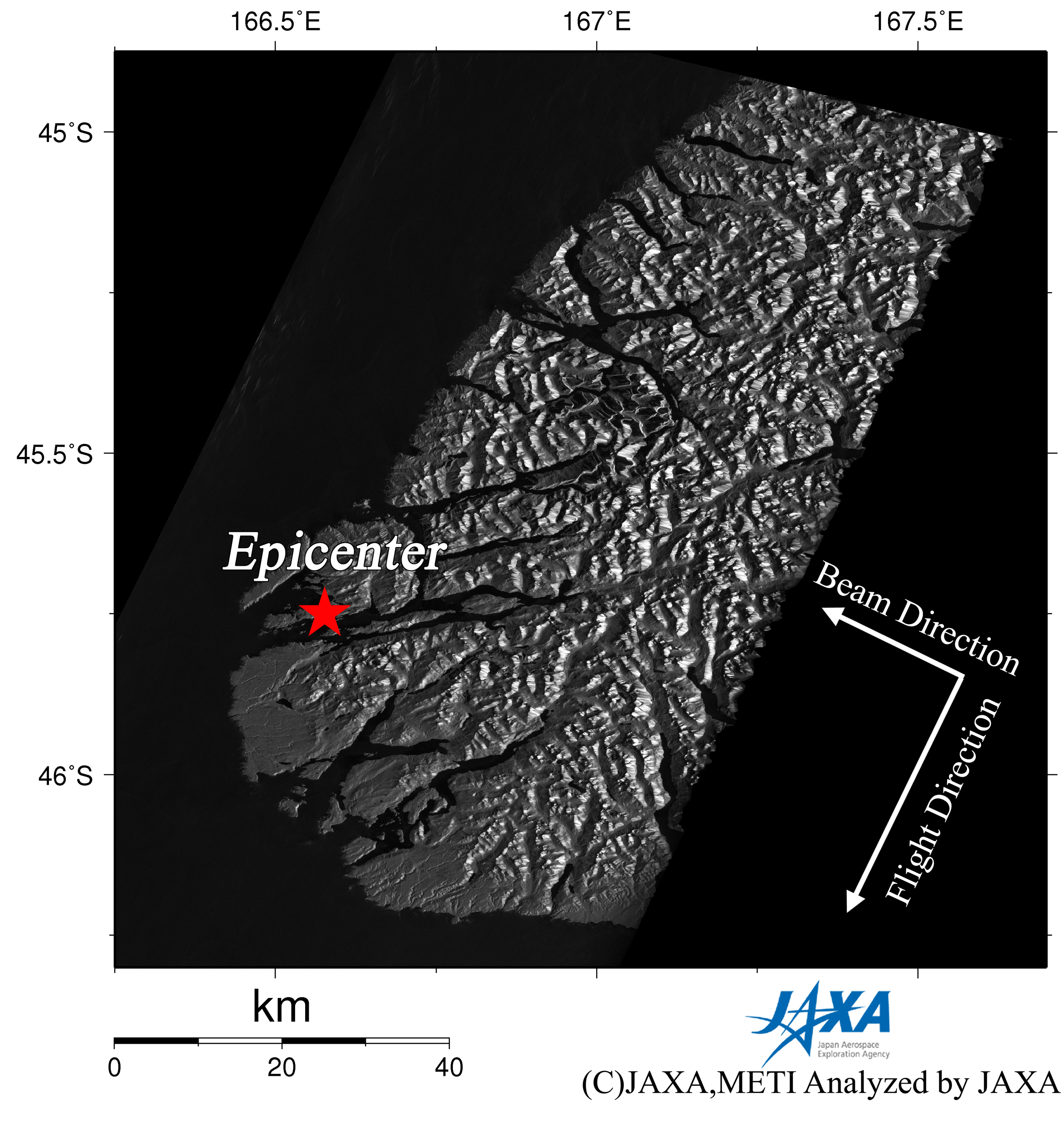
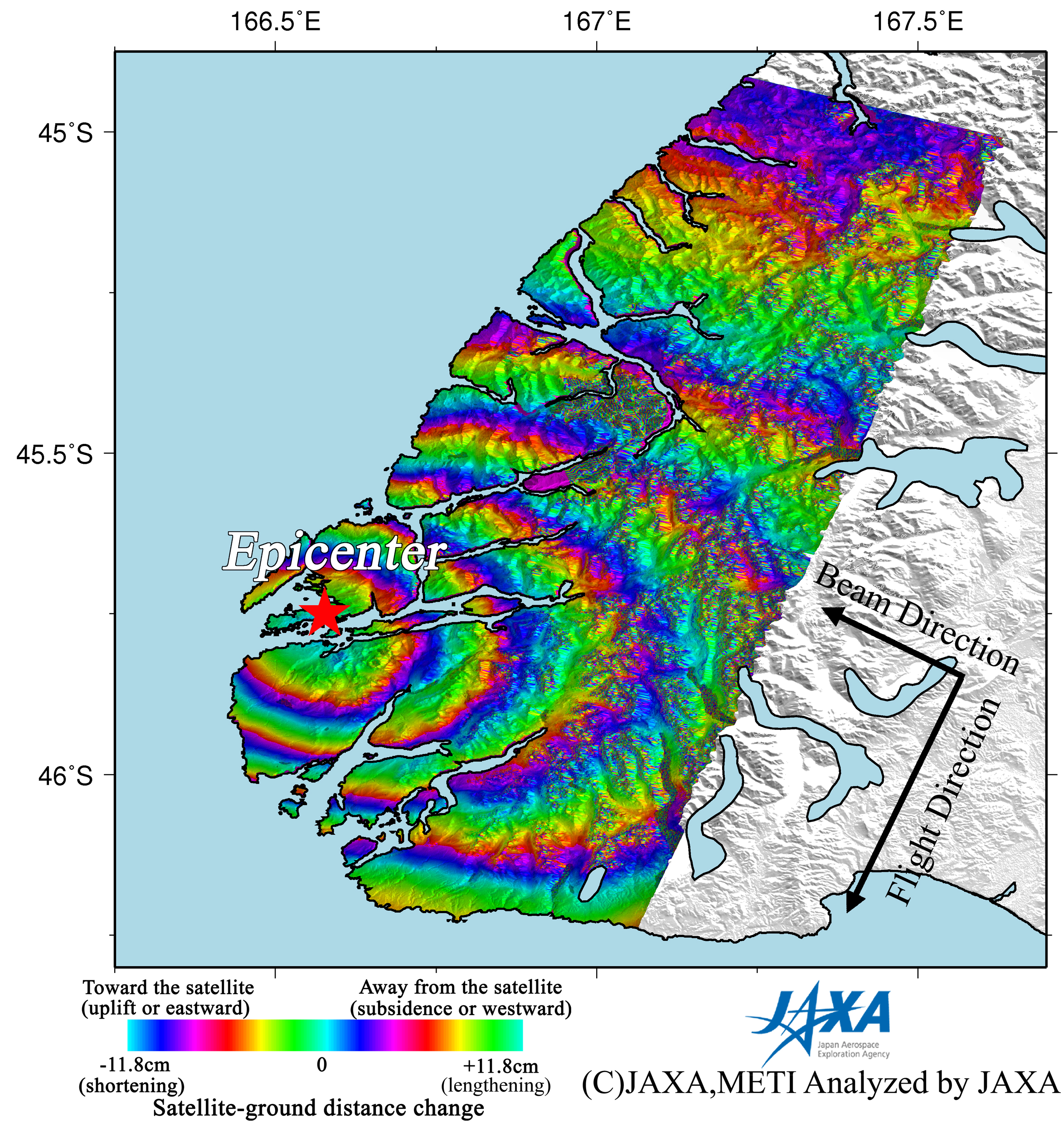
Figure 1 left is an interferogram generated from PALSAR data acquired before and after the earthquake using the DInSAR technique. A color pattern illustrates changes of satellite-ground distance for the period. Figure 1 right is a PALSAR amplitude image acquired after the earthquake indicating an observation field of 150 km from north to south. In the interferogram (Fig. 1 left), there are concentric fringes centered on the epicentral area. This color pattern is interpreted to represent an extension of satellite-ground distance. This indicates about 64.9 cm of crustal deformation, including a westward displacement caused by the seismic faulting.
JAXA plans to continue ALOS observations of the afflicted area in the southwest of New Zealand.
* The color changes from blue to red, yellow, green, and back to blue indicate an extension of the satellite-ground distance, and one color cycle is equal to 11.8 cm.
RELATIVE SITE
JAXA EORC