- Top
- Disaster
- 2011
- Emergency Observation of Shinmoedake peak (Kirishima Volcanic Range) Eruption by AVNIR-2 onboard "Daichi" (ALOS)
Emergency Observation of Shinmoedake peak (Kirishima Volcanic Range) Eruption by AVNIR-2 onboard "Daichi" (ALOS)
A small-scale eruption occurred in the Shinmoedake paek of Kirishima volcanic range on the border between Miyazaki and Kagoshima Prefectures at 1:27 (JST) on January 19 or 16:19 (UTC) on January 18, 2011. After that, explosive eruptions are continued with a big aerial vibration. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) has performed the emergency observation to monitor the state of the eruptions by the Advanced Visible and Near Infrared Radiometer type 2 (AVNIR-2)*1 onboard the Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS, "Daichi") at 11:19 on January 31, further to January 21, 23, 24, and 29, 2011 (JST).
Unfortunately Shinmoedake and ruined areas were not confirmed in acquired images on January 21, 23, 24, and 29, 2011 due to a lot of clouds.
Fig. 1 shows an observed image by AVNIR-2 on January 31, 2011 (JST), which is assigned band 3, 2 and 1 as the true color composite.
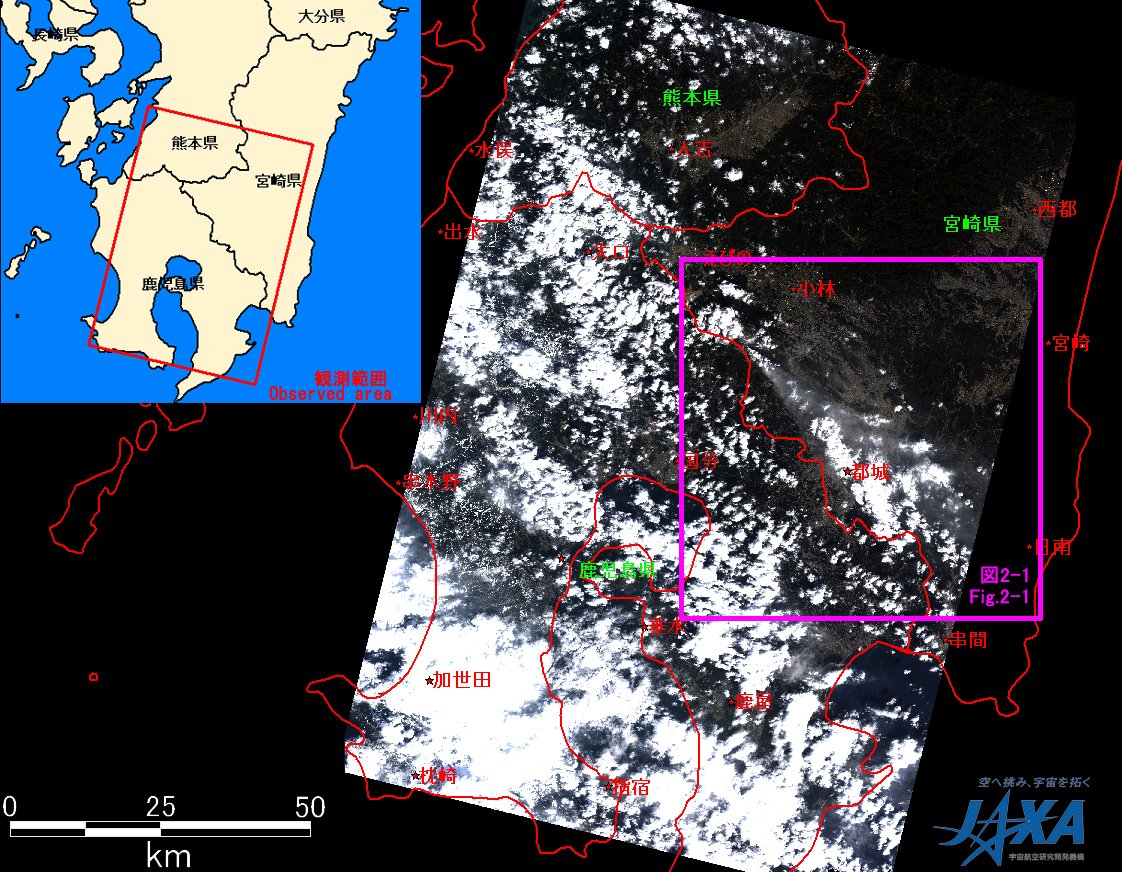
Fig.1: AVNIR-2 image with 27 degree pointing angle acquired at 11:19 on January 31, 2011 (JST).
The purple square shows the location of Fig. 2.
(Click to view enlarged image)
Fig. 2-1 is an enlarged image around Shinmoedake peak, which was compared image taken after eruption on January 31, 2011 (left) and before the eruption on December 29, 2009 (right). This image shows volcanic fumes from eruptive crater spread to southeastward. Also Fig. 2-2 shows volcanic fumes extended to around Miyazaki-city and was observed immediately before an explosive eruption on January 30, 2011.
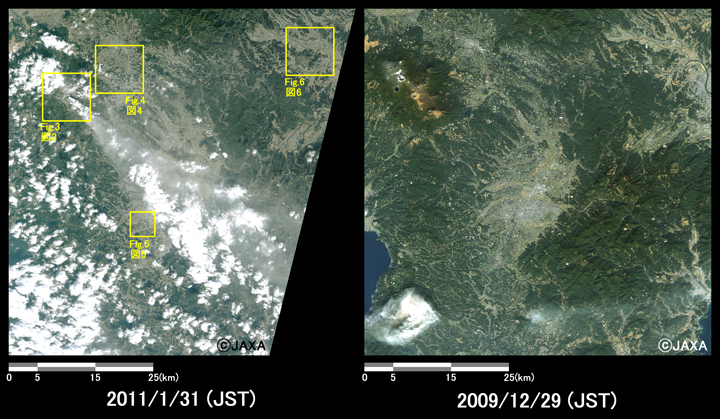
Fig.2-1: Enlarged images of Shinmoedake peak.
(3600 square kilometers, left: January 31, 2011; and right: December 29, 2009).
The yellow squares show the location of Figs. 3 to 6.
(Click to view enlarged image)
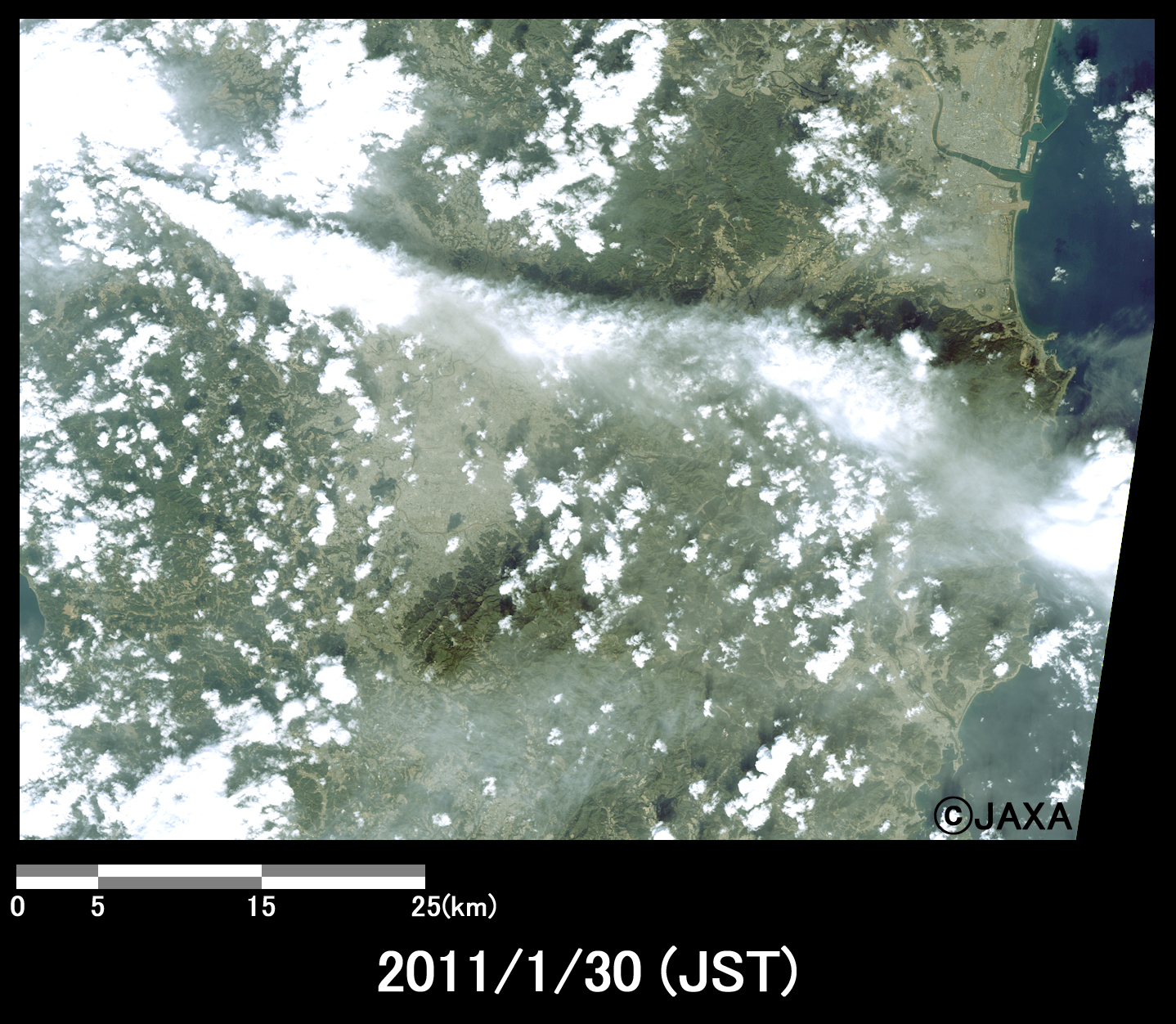

Fig.2-2: Enlarged image of Shinmoedake peak.
(50x70 kilometers, January 30, 2011).
(Click to view enlarged image)
Fig. 3 is an enlarged image of eruptive crater, which were acquired on January 31, 28, 2011, and December 29, 2009 from left to right. It is assigned band 4, 3 and 2 of AVNIR-2 as the false color composite, therefore vegetation can be seen in red color. The shape of crater and volcanic fumes can be identified from this image.
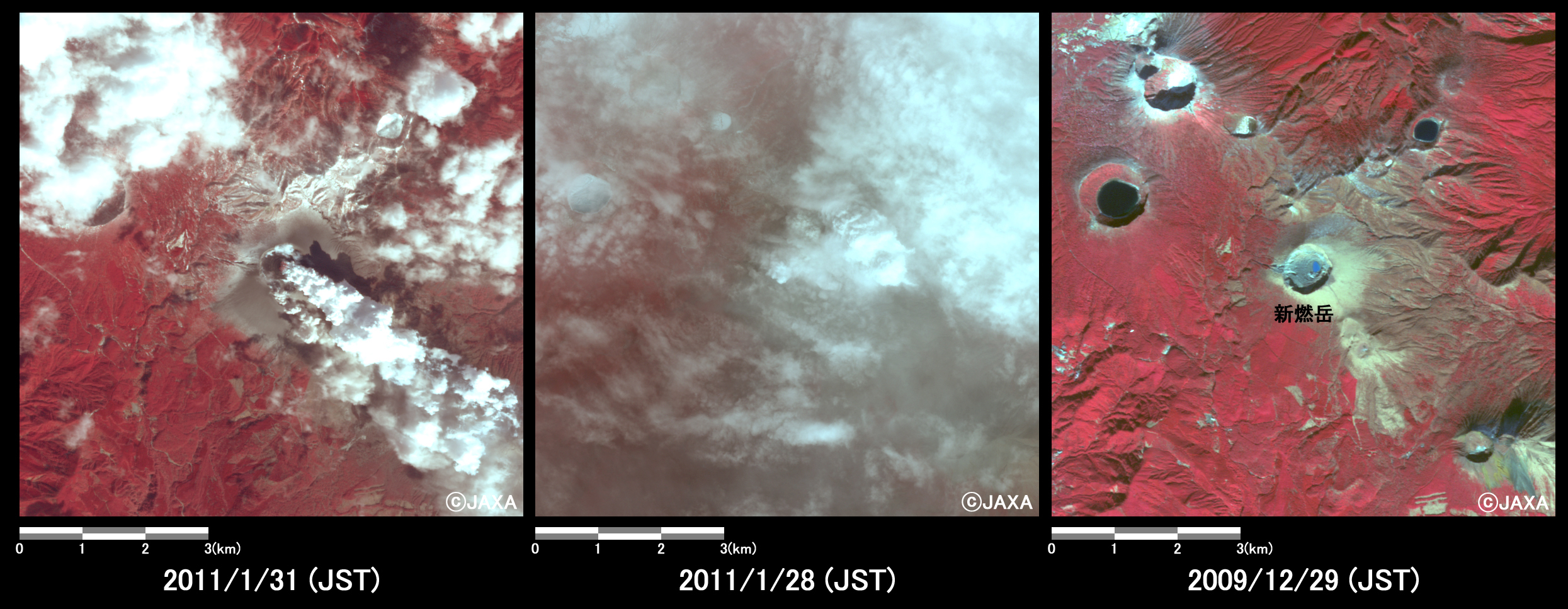
Fig.3: Enlarged image of Shinmoedake peak.
(64 square kilometers, left: January 31, 2011; center: January 28, 2011; and right: December 29, 2009).
(Click to view enlarged image)
Figs. 4 to 6 show enlarged images of ash fall area, which were compared images taken after eruption and before the eruption. The areas are located in eastern part of Shinmoedake peak (10 km east from the volcanic crater, Fig. 4), western part of Miyakonojo (5 km west from center of Miyakonojo, Fig. 5), and western part of Miyazaki (10 km north-west from center of Miyazaki City, Fig. 6), respectively.
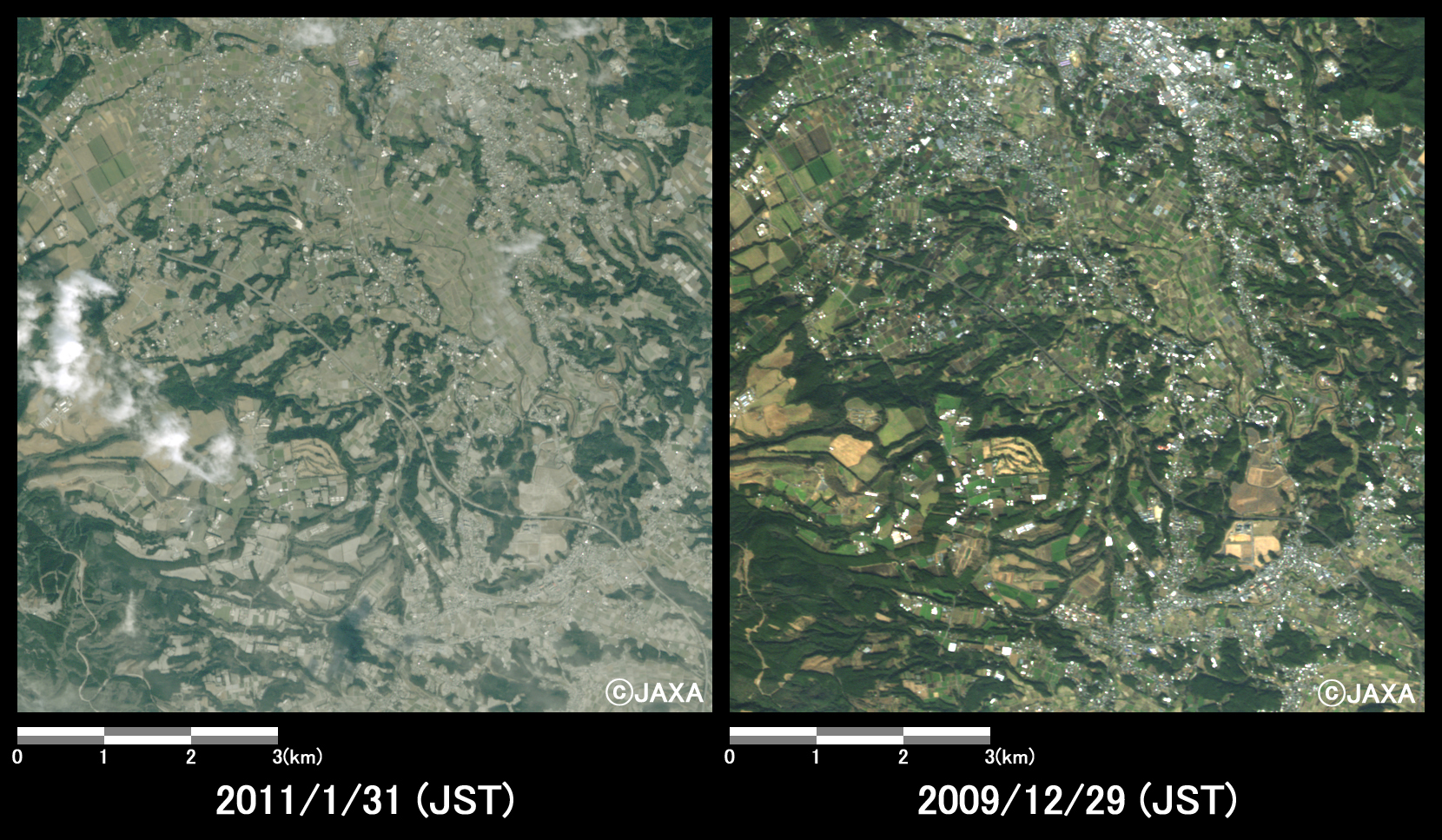

Fig.4: Enlarged image of eastern part of Shinmoedake peak.
(64 square kilometers, left: January 31, 2011; right: December 29, 2009).
(Click to view enlarged image)
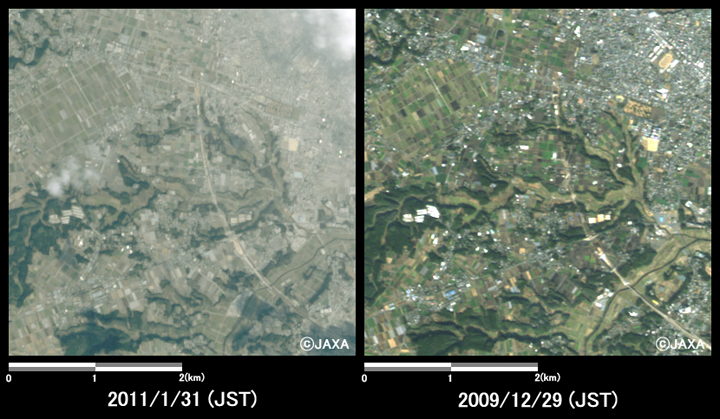

Fig.5: Enlarged image of western part of Miyakonojo City.
(16 square kilometers, left: January 31, 2011; right: December 29, 2009).
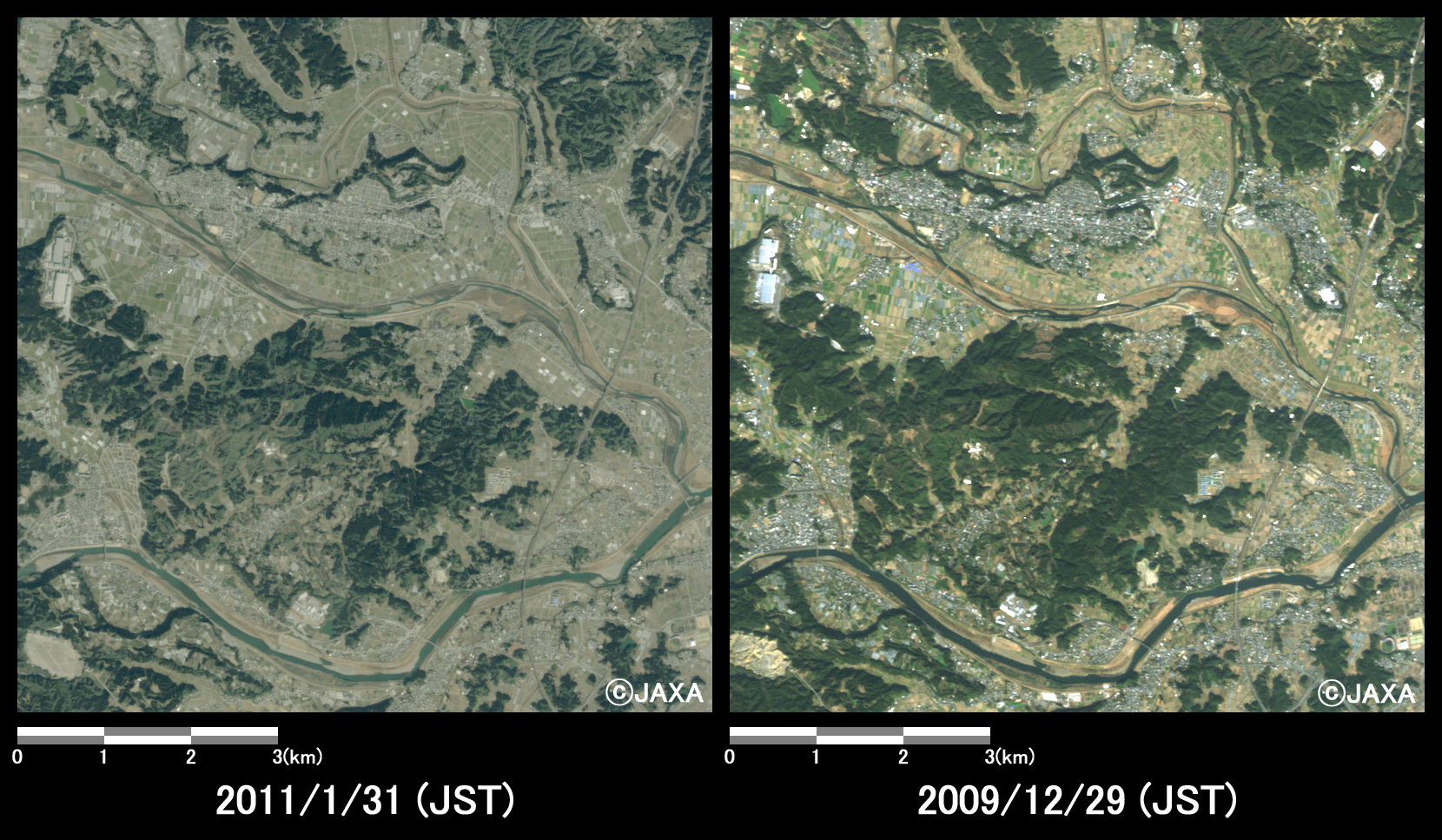

Fig.6: Enlarged image of western part of Miyazaki City.
(64 square kilometers, left: January 31, 2011; right: December 29, 2009).
(Click to view enlarged image)
The acquired images were provided to the Cabinet Secretariat, the Japan Meteorological Agency, the National Institute for Land and Infrastructure Management, the Public Works Research Institute, and Miyazaki prefecture.
Fig. 7 is image of Shinmoedake peak, which was taken after eruption by the Greenhouse gases Observing SATellite (GOSAT, "IBUKI")*2 at 13:26 (JST) or 4:26 (UTC) on January 26, 2011. The red triangle in Fig. 7 indicates the mountain range in Shirmoedake peak.
Fig. 8 is image of Shinmoedake peak, which was taken after eruption by the GOSAT at 13:26 (JST) or 4:26 (UTC) on January 29, 2011. This image shows volcanic fumes from eruptive crater spread to southeastward.
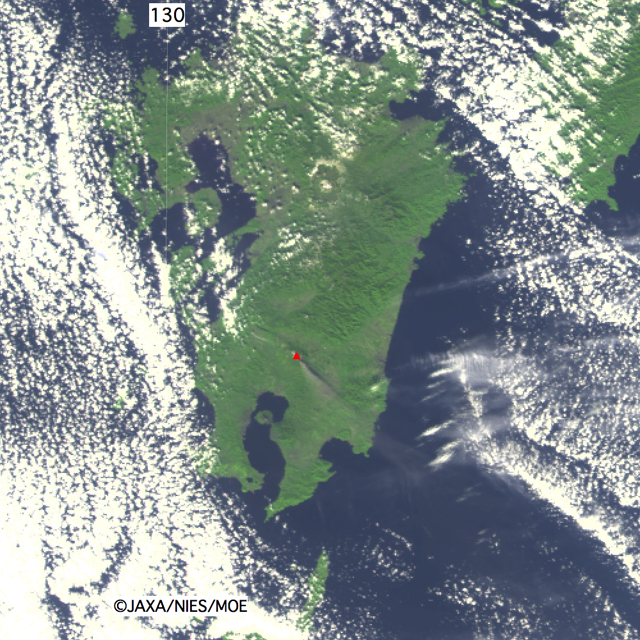
Fig.7: Observed image by GOSAT at 13:26 on January 26, 2011 (JST).
Sensor: Thermal And Near infrared Sensor for carbon Observation - Cloud and Aerosol Imager (TANSO-CAI)
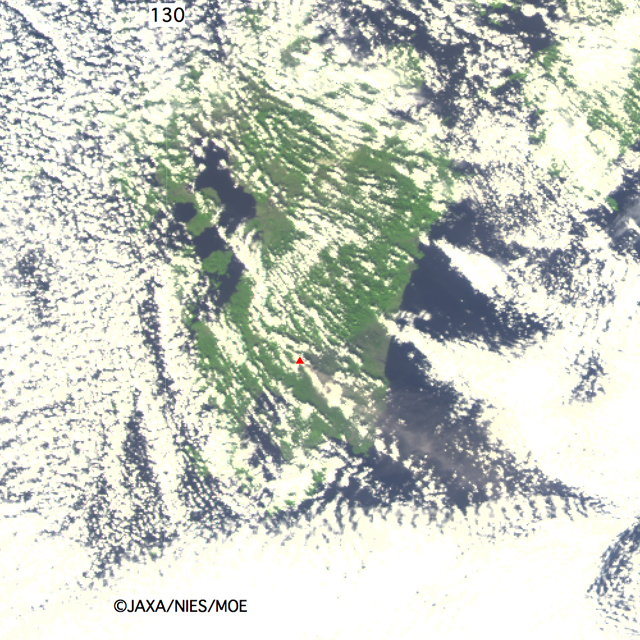
Fig.8: Observed image by TANSO-CAI onboard GOSAT at 13:26 on January 29, 2011 (JST).
* Advanced Visible and Near Infrared Radiometer type 2 (AVNIR-2):
AVNIR-2 is a visible and near infrared radiometer for observing land and coastal zones.
It provides 10 m spatial resolution with 70 km observing swath width on the ground. AVNIR-2 has the pointing angle change function from +44 to - 44 degrees.
* The Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite "IBUKI" (GOSAT):
GOSAT is the world's first spacecraft to measure the concentrations of carbon dioxide and methane, the two major greenhouse gases, from space. The spacecraft was launched successfully on January 23, 2009, and has been operating properly since then. The GOSAT Project is a joint effort of the Ministry of the Environment (MOE), the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES), and JAXA.








