Image Library
Mt. Merapi volcano, Indonesia observed by PALSAR and AVNIR-2 on April 29, 2006
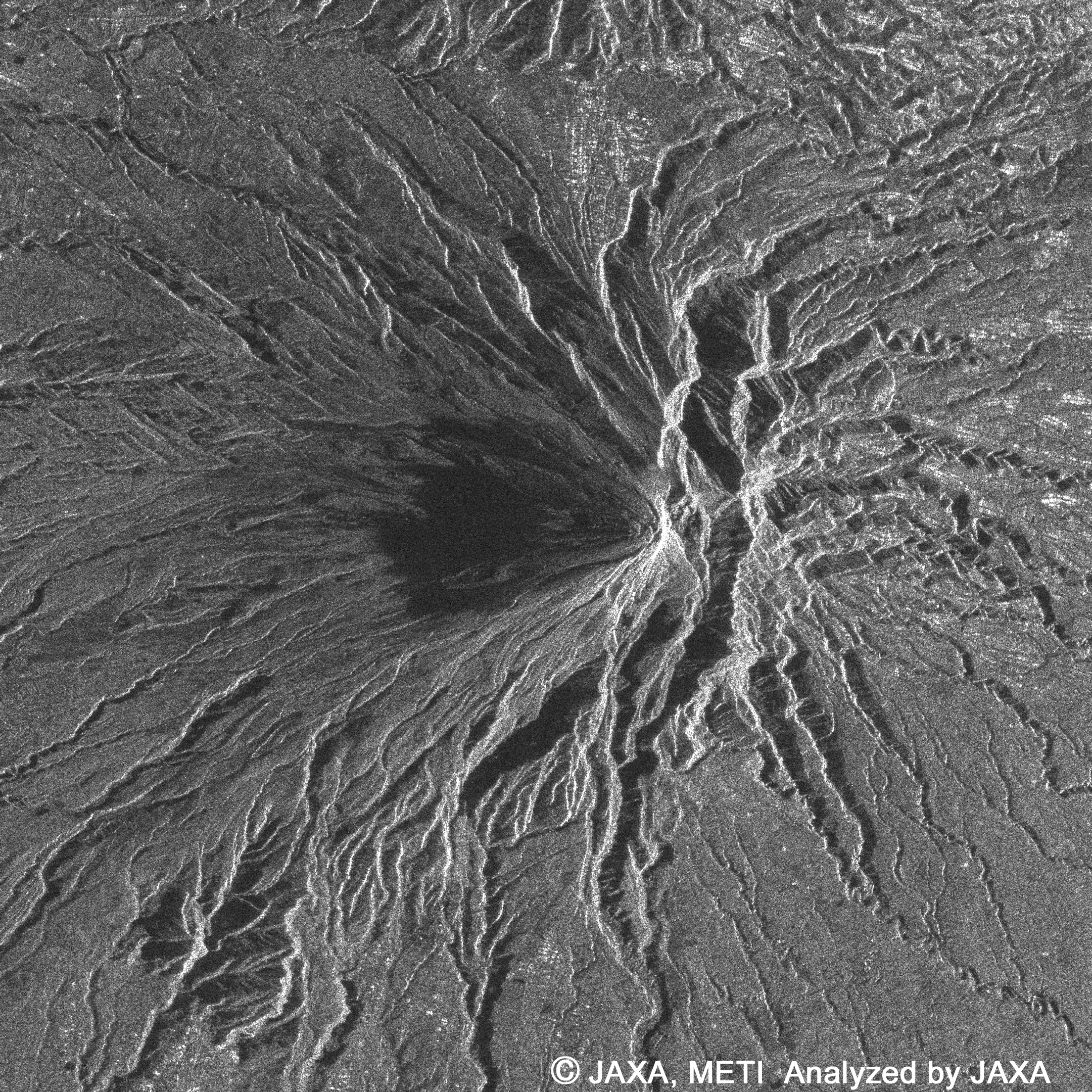
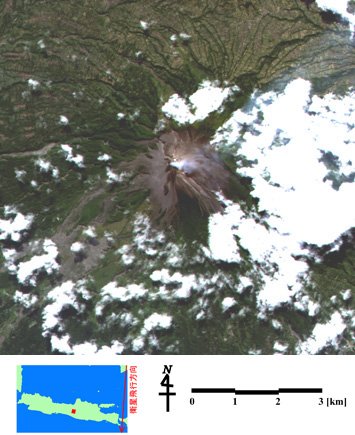
The above images were taken by the Advanced Visible and Near Infrared Radiometer type 2 (AVNIR-2) (right) and the Phased Array type L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) (left) at 11:40 a.m. on April 29, 2006 (Japan Standard Time, JST.).
According to the Directorate of Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, Indonesia (DVGHM), the crater cracked, and volcanic fumes were rising about 100 meters high from the crater on April 11. The AVNIR-2 observation data (right) clearly shows the fumes as well as volcanic ash at the crater and its surrounding area.
The PALSAR data (left) also clearly shows the undulating geographical character as radar reflection spreading radially from the crater to the foot of the mountain. The west side of the crater (on the left side of the crater in the image) is dark meaning weaker radar reflection, and that is considered to indicate different characteristics of the land surface.
The Merapi Mountain was named by combining the words "merah" (meaning "red") and "api" (meaning "fire"), and it is one of the most active volcanoes in Indonesia. There was a massive eruption in 1969 and it has repeatedly erupted once every two to three years since 1992. Every time lava erupts from the crater, it causes frequent damage including a collapse of a lava dome and destruction from a pyroclastic flow or a landslide.