ALOS-3
Wide-swath and High-resolution Optical Imager Overview and Main specifications
About Wide-swath and High-resolution Optical Imager
Major improvements over ALOS
- (1) Larger optical system
- (2) Higher performance detectors
- (3) Additional bands (4 bands to 6 bands)
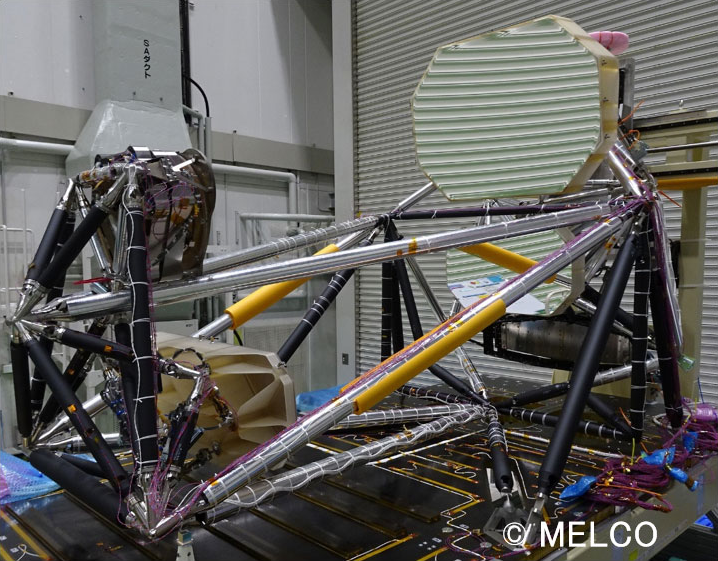
Off-axis four-mirror optical system
The "off-axis four-mirror optical system" was adopted based on the off-axis three-mirror optical system technology established by ALOS to achieve both high resolution and wide field of view. The combination of a sensor with a ground resolution of 0.8m and an observation width of 70km is one of the major features of ALOS-3.

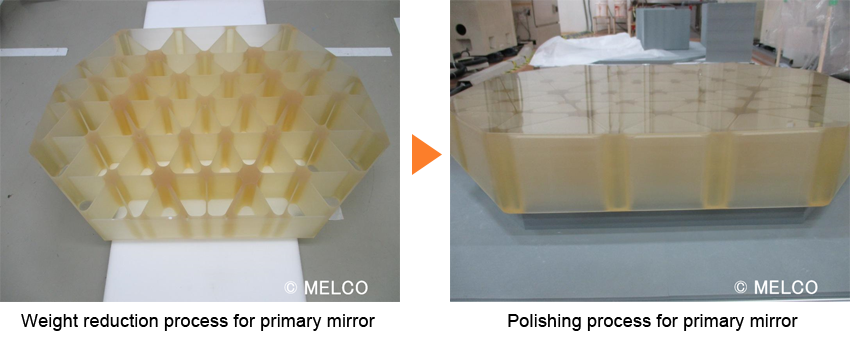
Mirror weight reduction and polishing
It is very important to reduce the weight of a satellite because the heavier the satellite is, the more fuel is required for launch and the more expensive it is to launch. In particular, the mirror is the heaviest part of the optical sensor. To reduce the weight of the mirror while maintaining its strength, the mirror is processed into a honeycomb structure. After the weight reduction process, the surface of the mirror is polished to make it smooth. Finally, the surface is polished until the surface accuracy error is reduced to 0.010µm.
Additional bands
ALOS-3 expands the number of observation bands of the optical sensor from the four of ALOS to six, which enables us to see more bands. As for the two additional wavelengths, the Coastal band is expected to be useful for observing underwater and coastal environments, and the RedEdge band is expected to be useful for understanding the activity of vegetation.
| ALOS-3 | ALOS |
|---|---|
Panchromatic band (black and white)520-760nm
|
Panchromatic band (black and white)520-770nm
|
Multi-band (color)Band 1: 400-450nm (Coastal)
Band 2: 450-500nm (Blue)
Band 3: 520-600nm (Green)
Band 4: 610-690nm (Red)
Band 5: 690-740nm (Red Edge)
Band 6: 760-890nm (NIR)
|
Multi-band (color)
Band 1: 420-500nm (Blue)
Band 2: 520-600nm (Green)
Band 3: 610-690nm (Red)
Band 4: 760-890nm (NIR)
|
ALOS-3 Observation Modes
Various Observation Modes
 Strip-map observation mode (STM)
Strip-map observation mode (STM)The satellite can normally perform observation covering 70 km in width and 4,000 km in along-track direction as the strip-map observation mode.
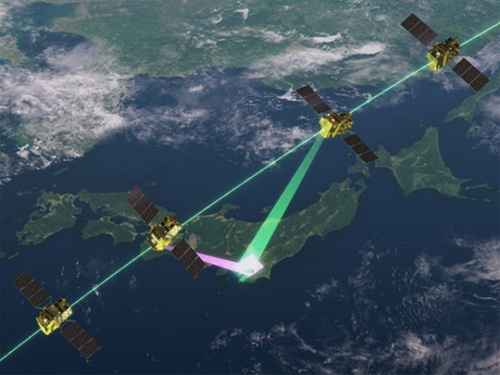 Stereoscopic observation mode in single orbit path (3D1)
Stereoscopic observation mode in single orbit path (3D1)Acquisition of stereo pair images of one or more scenes of the same location from two different observation directions in a single path.
 Stereoscopic observation mode in two orbit paths (3D2)
Stereoscopic observation mode in two orbit paths (3D2)Combining two strip-map observations by nadir and backward view in the neighboring path after three days i.e., sub-cycle revisit orbit.
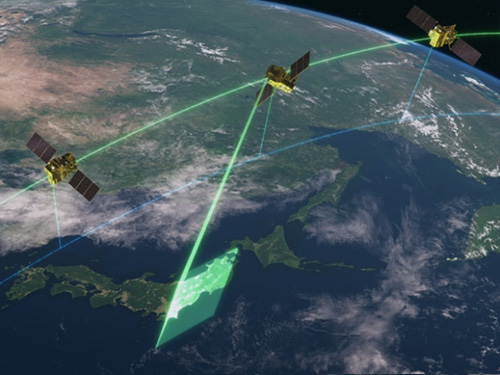 Pointing observation mode(PNT)
Pointing observation mode(PNT)The satellite can observe there using pointing capability within 60 deg if the user has a certain ground point or an area of interest (AOI)
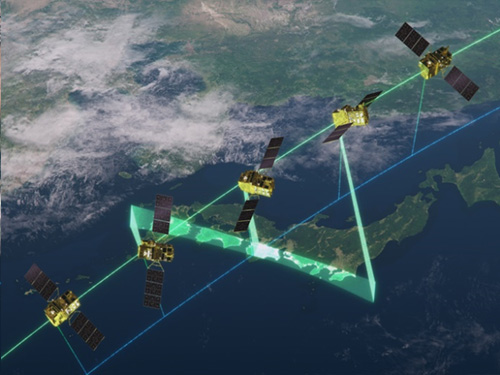 Changing direction observation mode(DRC)
Changing direction observation mode(DRC)The satellite can observe any given area by the pointing capability up to 60 deg. in all directions against the satellite nadir. In the case of Japan, it can be activated within 24 hours after receiving the request. This mode will be used when a large natural disaster happens e.g., the expecting Nankai Trough large earthquake.
 Wide-area observation mode (WID)
Wide-area observation mode (WID)This mode can cover in a wide-ranging area of 200 km (in along-track direction) x 100 km (in cross-track direction) by satellite’s single orbital passage.