
![[Prev Page]](http://www.eorc.nasda.go.jp/images/PrevPage.gif)
![[Next Page]](http://www.eorc.nasda.go.jp/images/NextPage.gif)
![[Top Of
Page]](http://www.eorc.nasda.go.jp/images/TopOfPage.gif)
![[ADEOS Home]](../../images/ADEOS_HomePage.gif)
![[EORC Home]](../../images/EORC_HomePage.gif)
![[Directory]](../../images/Directory.gif)
Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS)
provided by NASA
| 
|
Observation Concept
Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) is an optical sensor to measure the
albedo of the earth's atmosphere at six narrow spectral bands. The total ozone
content is interrelated with changes of solar radiation in the near ultraviolet
wavelengths so that the spatial distribution of the total ozone can be inferred
by observing several near UV bands. In addition, the TOMS observation data can
be used to make quantitative estimates of sulfur dioxide gases in the near UV
band.
The FOV of TOMS is 3 x 3 degrees (swath width : 42 x 42km) and its scanning
angle is +/- 55.5 degrees (approx. 2,800km of the ground surface) along the
track. This wide swath width can cover the entire earth surface in a day.
Planned Missions
The primary object of TOMS is to collect data of the global ozone content and
sulfur dioxide continuously. Combined with monitoring of ozone depletion in the
south pole, which has been recently addressed as one of immediate environmental
issues, and changes of ozone content after implementation of CFC Protocol, the
data can be used for the quantitative analysis of factors related to the ozone
issues and the potential effects of volcanic eruptions on climatic changes.
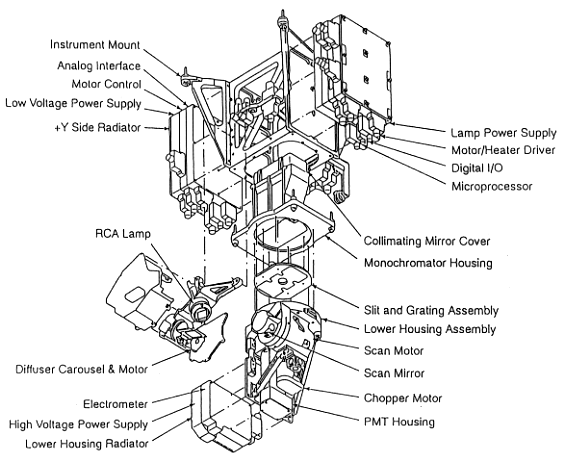
Configuration and Function of Sensor
TOMS consists of optical subsystem, electrical subsystem and driving subsystem.
|
TOMS overview
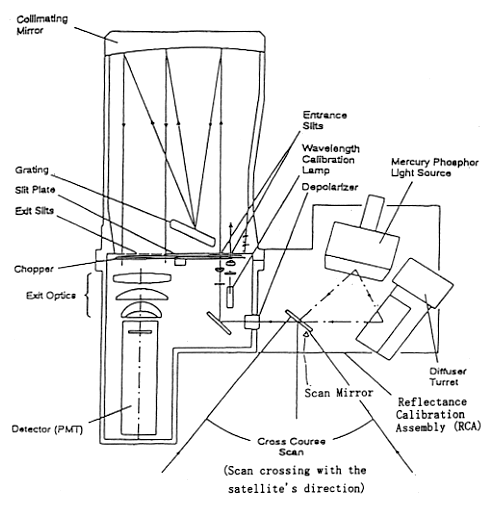
| | TOMS optical system
| |
The scan mirror observes the earth target along cross track direction, and first
focuses sun light on the right side of a collimator. The spectrum, using
holographic grating, is focused on the other side of the collimator and
converted to the electrical signals via optoelectronic amplifier in the focal
plan. Each spectrum is focused on the focal plan via Slit Plates and Chopper.
The TOMS observation data will be calibrated by using one of three diffusers.
The alternative use is to evaluate degradation of the diffuser by solar
radiation. TOMS can also calibrate by using mercury phosphor and wavelength
calibration is made by using a reflectance calibrator.
![[Prev Page]](http://www.eorc.nasda.go.jp/images/PrevPage.gif)
![[Next Page]](http://www.eorc.nasda.go.jp/images/NextPage.gif)
![[Top Of
Page]](http://www.eorc.nasda.go.jp/images/TopOfPage.gif)
![[ADEOS Home]](../../images/ADEOS_HomePage.gif)
![[EORC Home]](../../images/EORC_HomePage.gif)
![[Directory]](../../images/Directory.gif)
 Earth Observation Research Center
Earth Observation Research Center
Comments to: adeossupport@eorc.nasda.go.jp
Last Update: 5 Febrary 1998





![]() Earth Observation Research Center
Earth Observation Research Center