

|
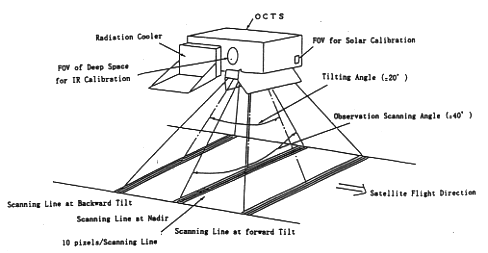
| OCTS observation concept. |
The satellite flying over the equator cannot get inforamtion on the ocean
because of direct sunglitter at the sea surface. In order to prevent this
sunglitter from interrupting the observation, OCTS can tilt its field of view
along the track by +/- 20 degrees.
It is likely that sensor performance is subject to the unique space
environmental factors, such as radiation, affecting detector sensitivity and
mirror transmittance. OCTS has optical calibration functions using solar light
and halogen lamp so as to perform as planned in visible and near-infrared bands.
For example, when the satellite passes over the north pole, solar light enters
the solar calibration module so that the deep space and black body are observed
every rotation of a mirror so as to calibrate differences between lower
temperature and ambient temperature.
In addition, OCTS has electrical calibration functions to confirm performance of
the electrical unit. OCTS has two data transmission modes. All raw pixel data is
transmitted via Direct Transmission Subsystem (DT) or Inter Orbit Communication
Subsystem (IOCS) in fine data transmission mode. One pixel data is sampled from
every 6 x 6km area as typical data of the area and is downlinked to the local
users (ex. fishery ships) via Direct Transmission to Local Users (DTL) in
coarse data transmission mode.
Note) Phytoplankton in the ocean convert nutrients into plant material which feeds various fishes, such as sardines and tuna. Thus, Phytoplankton is an indicator of ocean productivity.
|
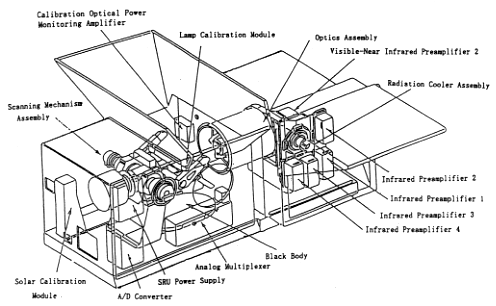
| Internal configuration of SRU. |
The scanning mirror reflects observation light to focus on Optics Assembly. The
mirror is electrically rotated per second and scans a line at forward and
backward tilt within +/- 20 degrees. In the Optics Assembly, light is converged
through Ritchie-Chretien telescope and then splitted to two visible-near
infrared bands and a infrared band through a dichroic filter. In Visible and
Near Infrared Detector Assembly, optical signals are converted electrically.
The infrared detector is cooled at 100K by a large radiation cooler. It faces
the deep space at temperature of 4K, and emits heat of the detector. The
electrical signals are amplified by the specefied gain in Analog Signal
Processor, and then converted to digital signals. The digital signals processed
in Digital Signal Processor are transmitted to bus module.
![]() Earth Observation Research Center
Earth Observation Research Center