 | |||||||
     | |||||||
| About Us | About GDaWG | GPM Overview | Background and Objectives | Membership | Activities | ||
| GPM Overview | ||
|
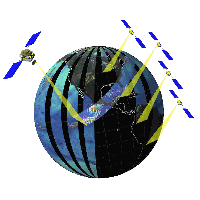
GPM is, like TRMM, composed of one sun non-synchronous orbit
satellite (a core satellite)-borne a precipitation radar and a
microwave scanning radiometer, and more than one sun synchronous
orbit satellite-borne a microwave scanning radiometer (constellation
of sub-satellites). |
 | |
|
The core satellite is expected to be able to measure detailed precipitation activities, using both of the dual frequency precipitation radar and the microwave scanning radiometer. The data acquired by such measurement will permit of sophisticating the presumed algorithm of quantitative rain measurement in the microwave scanning radiometer. The sub-satellite will conduct the precipitation measurement of the microwave scanning radiometer and the measurement will become more reliable by utilizing the presumed algorithm. The sub-satellite constellation will be launched by NASA and
other space organizations in the world. The number of satellites
will be around eight. lt is possible to get a global rainfall
distribution in every 1 hour when the microwave scanning
radiometers aboard these 8 polar orbit satellites collect and
process the data. GPM plans real-time transmission of the global
rainfall distribution data. This real-time data can be utilized not
only for scientific research, but for social fields, including
weather forecast, flood prediction, water resource
management. | ||
|
Copyright (c) 2008 JAXA EORC All Rights
Reserved. |