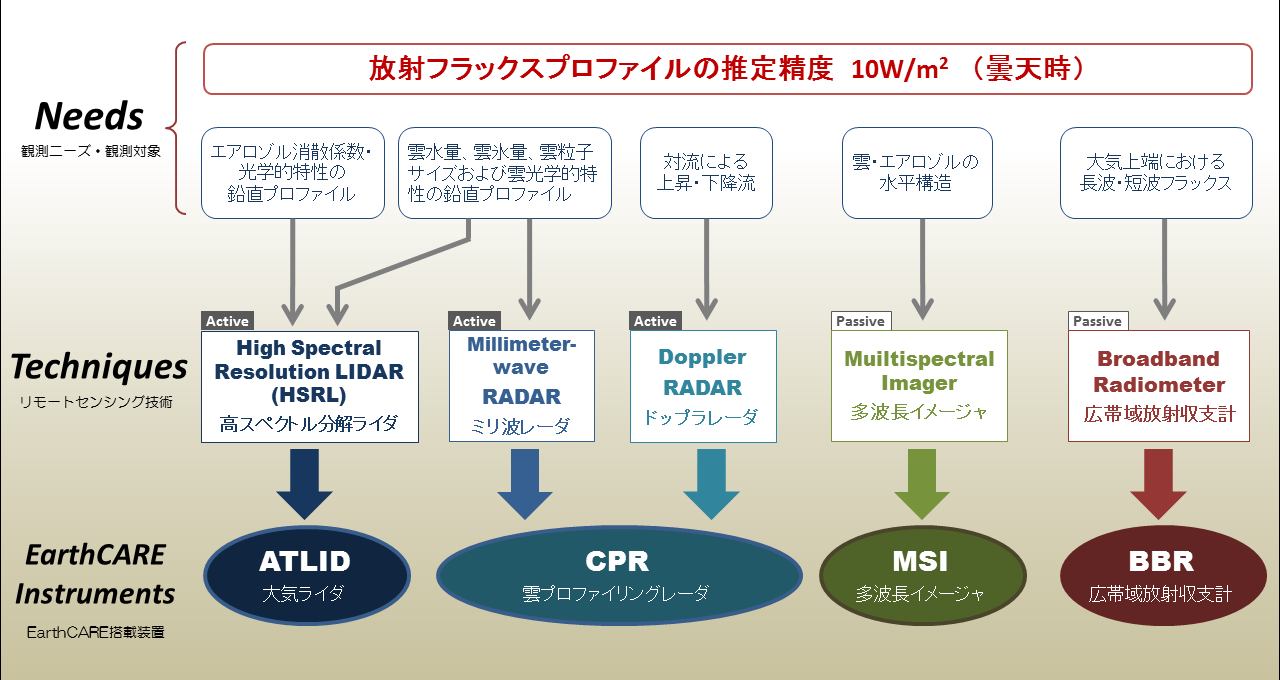
The following figure outlines the measurement technology corresponding to the observation target and the specifically designed EarthCARE observation equipment.
- Top
- Mission
- Synergistic observation with four sensors
Synergistic observation with four sensors
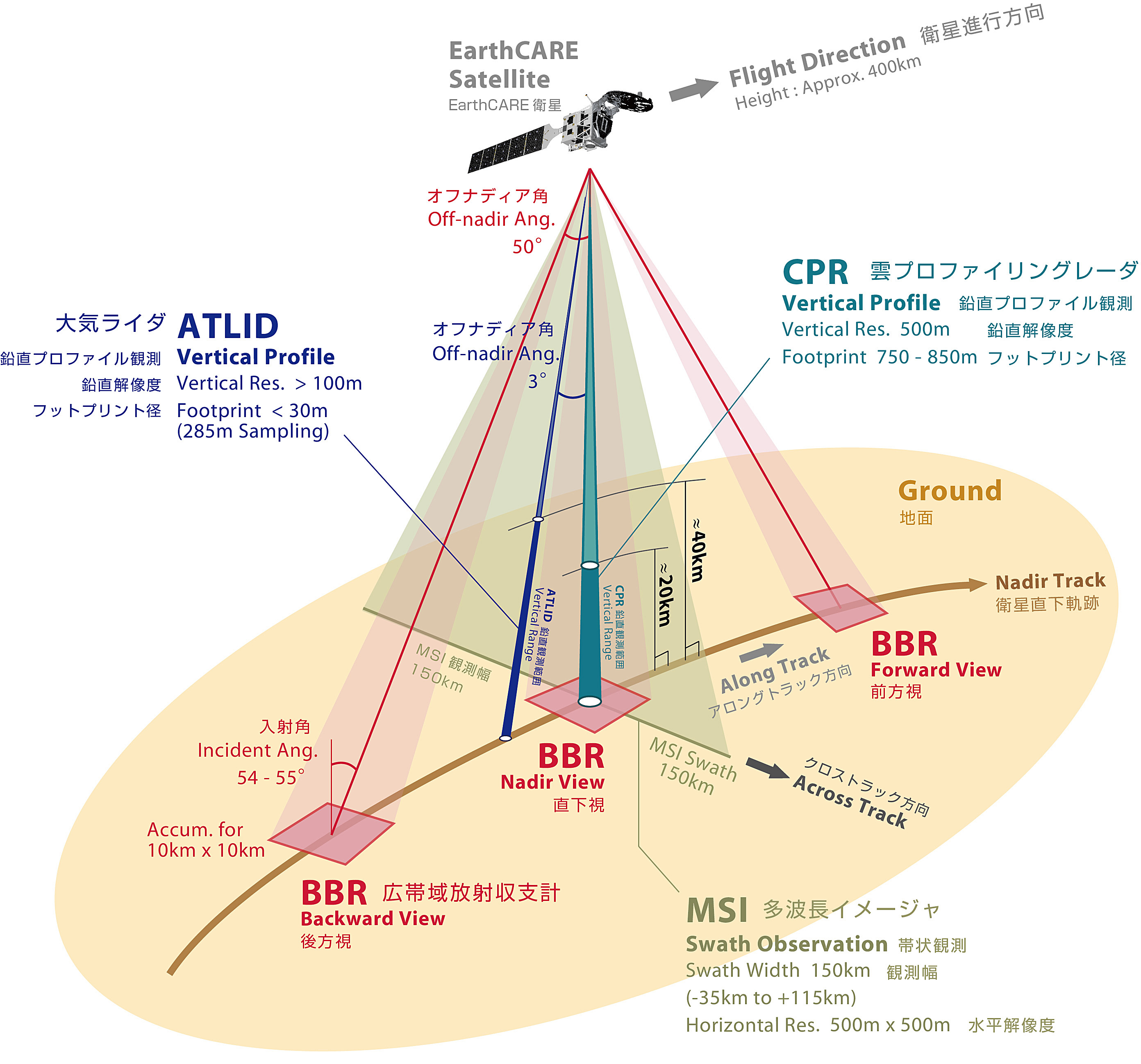
The EarthCARE satellite's observations are characterized by radar, lidar, imager, and broadband radiometer. This results in synergy products that combines the data from these instruments. We conduct synergetic (synchronous) observations from all sensors almost simultaneously to obtain observation data that are nearly identical in the location of the target.
Horizontal and vertical distributions and characteristics of clouds and aerosols ... CPR, ATLID, MSI
To measure the vertical profiles of cloud and aerosol distribution and characteristics, an active sensor is required that transmits signals from the instrument. EarthCARE targets clouds and aerosols. The size of the detected particles depends on the wavelength of the transmitted wave.
Clouds and aerosols have particle sizes from 10 nm to 0.1 mm in diameter, and it is necessary to prepare suitable observation equipment for each particle diameter range.
Radar in the 94 GHz band has a wavelength of approximately 3.2 mm and is highly sensitive to most types of clouds. It is also sensitive to drizzle and light rain, which are slightly larger than cloud particles.

Aerosols, on the other hand, have even smaller particles than clouds, making short-wavelength lidar more effective than radar. Lidar using 355 nm ultraviolet light is sensitive to aerosols and very thin clouds, such as the cirrus types.
A key feature of EarthCARE's instrument design is the capability to obtain more accurate data by combining the advantages of simultaneous observations by radar and lidar.
Combining cloud and aerosol horizontal distribution data from the imager with selected channels for atmospheric observation can supplement radar and lidar observations, which can only provide data directly below the satellite, and reproduce three-dimensional information.
Upward and downward flow due to atmospheric convection ... CPR
Doppler weather radar can detect local wind movement using the Doppler effect of particle motion and is used at airports. EarthCARE is expected to provide information on vertical wind strength based on the vertical movement of cloud particles with a millimeter-wave radar having a Doppler velocity measurement function.
Radiation balance at the top of the atmosphere ... BBR
The broadband radiometer measures the radiation at the top of the atmosphere. Obtaining upward radiation fluxes at the top of the atmosphere for shortwave (solar radiation) and longwave (terrestrial radiation) regions makes it possible to compare cloud and aerosol data obtained by radar, lidar, and imager with radiation observation.